Managing Remote Agent Appliances
In Oracle Cloud Migrations, a remote agent appliance collects metadata from virtual machines (VMs) from an external environment and replicates the VM data disks to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
The deployment of remote agent appliance requires installation and registration. After the agent appliance is registered with a source environment, the agent maintains a persistent secure connection back to OCI by performing a secure token exchange. These secure tokens are refreshed regularly. If the remote agent appliance is unable to refresh the authentication token, the agent is disconnected, and you must manually re-register from the remote agent appliance console. The remote agent appliance includes a diagnostic tool to help identify any network connectivity issues or problems communicating to OCI.
- Create a separate source environment for each region.
- Deploy at least one remote agent appliance for each target region.
After the remote agent appliance is registered and becomes active, the appliance launches two plugins namely, discovery and replication. The discovery plugin searches for VMware virtual machines in the source environment using environment-specific connectors. The replication plugin manages the replication of source assets snapshots from the source environment to OCI.
You can deploy multiple remote agent appliances for a single source environment to provide redundancy and increased replication throughput.
Prerequisites
DNS Resolution
For the replication to work, the Remote Agent Appliance must have connectivity to a
domain name system (DNS) server that resolves addresses for names in the
oraclecloud.com domain and the fully qualified domain names
(FQDN) of VMware infrastructure components (vCenter server and ESXi hosts).
To verify if your DNS resolution is working properly before deploying your virtual appliance, perform the following steps:
- Find the IP address of the DNS server that you intend to use (for example,
10.0.2.1). - Connect to the vCenter management interface, and find an FQDN used by a host (for example,
esx1.vcluster.mycompany.local). - To see if the name is properly resolved, run a DNS diagnostic tool. MacOS and
most Linux distribution have domain information groper (dig) tool preinstalled.
The dig that you can use for verification is,
dig @{dns_server_IP} {FQDN}. Example:dig @10.0.2.1 esx1.vcluster.mycompany.local
If correct IP address of the host is returned in the output, then your DNS resolution is working properly. To correctly configure the DNS, see DNS Requirements for the vCenter Server Appliance.
Required IAM Policies
You can create policies to allow user groups to access remote agent appliance resources.
View the verb to permission
mapping for remote agent appliance to decide which verb
meets the access requirements. For example, inspect allows users to view the
list of all the agents in a compartment and read allows users to view the
details of all plugins running on a specific agent.
For details about writing policies for Oracle Cloud Migrations, see Oracle Cloud Migrations IAM Policies. For users to access the Oracle Cloud Migrations resources, see user policies. For using the Oracle Cloud Migrations service, see service policies.
Required Network Connectivity in the External Environment
The remote agent appliance is distributed as a sealed virtual machine that requires IPv4 addresses to operate, which can be statically assigned or assigned using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
The remote agent appliance can be configured to use a single interface or isolated interfaces for internal and external connectivity. Internal connectivity is for communication with vCenter and ESXi host. External connectivity is for communication with Oracle Cloud public endpoints. To use a statically assigned IP, only a single interface can be used and needs to be able to route to both internal and external destinations. For manual configuration, see step 7 in the Details for Deploying an OVA or OVF Template section.
Following are the required vCenter configurations for networking ports, protocols, and direction that the remote agent appliance uses for connecting OCI with the external VMware environment:
The following diagram illustrates and list the ports required for proper operation of the remote agent appliance.
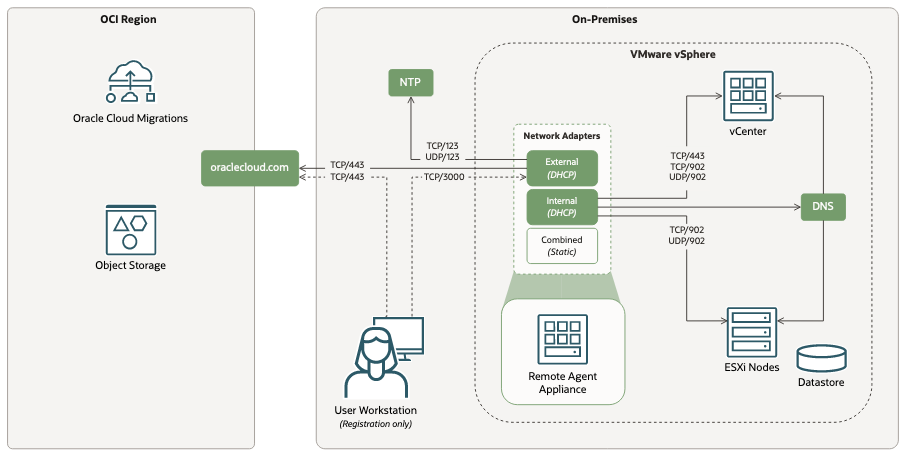
| Source | Destination | Port | Protocol | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| User Workstation | Remote Agent Appliance - External Interface | 3000 | TCP | Used for agent registration and agent reset. |
| Remote Agent Appliance | DNS Server | 53 | UDP, TCP | DNS resolution |
| Remote Agent Appliance | DHCP Server | 67, 68 | UDP, TCP | DHCP configuration |
| Remote Agent Appliance | NTP Server | 123 | UDP, TCP | NTP clock synchronization |
| Remote Agent Appliance - External Interface | oraclecloud.com | 443 | TCP | HTTPS connection to OCI |
| Remote Agent Appliance - Internal Interface | vCenter | 443 | TCP | HTTPS connection to vCenter |
| Remote Agent Appliance - Internal Interface | Egress | 902 | UDP, TCP | VDDK connection to vCenter and ESXi Hosts |
Default Listening Ports
- TCP port 443 - Use this port to configure vCenter Server Management API
- TCP/UDP port 902 - Use this port to configure the host or server access
The remote agent appliance does not support working vCenter configurations that use non-default ports.
Required vSphere Privileges
For the discovery and replication phases of migration, the remote agent appliance requires vCenter credentials. You can use the same user credentials for discovery and replication phases or create a user for each of these phases.
- Discovery: Create a user with a Read Only role. For information on how to create a user, see vCenter Server System Roles in VMware documentation.
-
Replication: For replicating assets, create a vCenter server custom role, such as Oracle Cloud Migrations. For information on how to create a custom role, see Create a vCenter Server Custom Role in VMware documentation.
The privileges that you must define for the role that you create are as follows:
-
Global: For the global category, select the following privileges:
- Disable methods
- Enable methods
- Licenses
-
Virtual machine: For the virtual machine category, select the following privileges:
- Change configuration: Acquire disk lease
- Provisioning: Allow read-only disk access
- Provisioning: Allow virtual machine download
- Snapshot management: Create snapshot
- Snapshot management: Remove snapshot
You can create a role by cloning an existing role. For example, you can clone the VMware Consolidated Backup user (sample role), add required global privileges, and then save the role as a new role for replication.
-
Global: For the global category, select the following privileges: