Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure Description
Learn how you can leverage the combined capabilities of Oracle Exadata and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure with Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure
- About Exadata Cloud Infrastructure
Exadata Cloud Infrastructure allows you to leverage the power of Exadata in the cloud. - Licensing Considerations for Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure
Subscription to Exadata Cloud Infrastructure can include all of the required Oracle Database software licenses, or you can choose to bring Oracle Database software licenses that you already own to Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure. - Supported Database Edition and Versions for Exadata Cloud Infrastructure
Exadata Cloud Infrastructure databases require Enterprise Edition - Extreme Performance subscriptions or you can bring your own Oracle Enterprise Edition software licenses. - Subscription Types
Available subscription types. - Metering Frequency and Per-Second Billing
Per-Second billing, minimums and limitations on billing. - Technical Architecture of Exadata Cloud Infrastructure Systems
Exadata Cloud Infrastructure systems integrate Oracle's Exadata Database Machine hardware with the networking resources needed to securely connect to your organization’s on-premise network and to other services in the Oracle cloud. - Scaling Options
Introduction to the Scaling option on Exadata Cloud Infrastructure. - System and Shape Configuration Options
Review the list of Exadata System Shapes
About Exadata Cloud Infrastructure
Exadata Cloud Infrastructure allows you to leverage the power of Exadata in the cloud.
You can provision flexible X8M and X9M systems that allow you to add database compute servers and storage servers to your system as your needs grow. X8M and X9M systems offer RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) networking for high bandwidth and low latency, persistent memory (PMEM) modules, and intelligent Exadata software. X8M and X9M systems can be provisioned using an shape equivalent to a quarter rack X8 or X9M system, and then database and storage servers can be added at any time after provisioning. For more information on X8M and X9M systems, see Overview of X8M, X9M, and X11M Scalable Exadata Infrastructure.
The RDMA software allows computers in a network to exchange data in main memory without involving the processor, cache, or OS of either computer. RDMA can improve throughput and performance because it frees up resources, and it can also facilitate a faster data transfer rate. RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) is the network protocol that allows RDMA over an Ethernet network.
X8 and X7 systems are also available in fixed-shapes (quarter, half, and full rack systems). These systems use InfiniBand networking, and do not have the ability to scale database and storage servers. You can also provision an Exadata base system, which has a smaller capacity than a quarter rack system.
For all Exadata Cloud Infrastructure instances, you can configure automatic backups, optimize for different workloads, and scale the OCPU and storage allocations as needed.
- Roles and Responsibilities for Exadata Cloud Infrastructure Software Maintenance
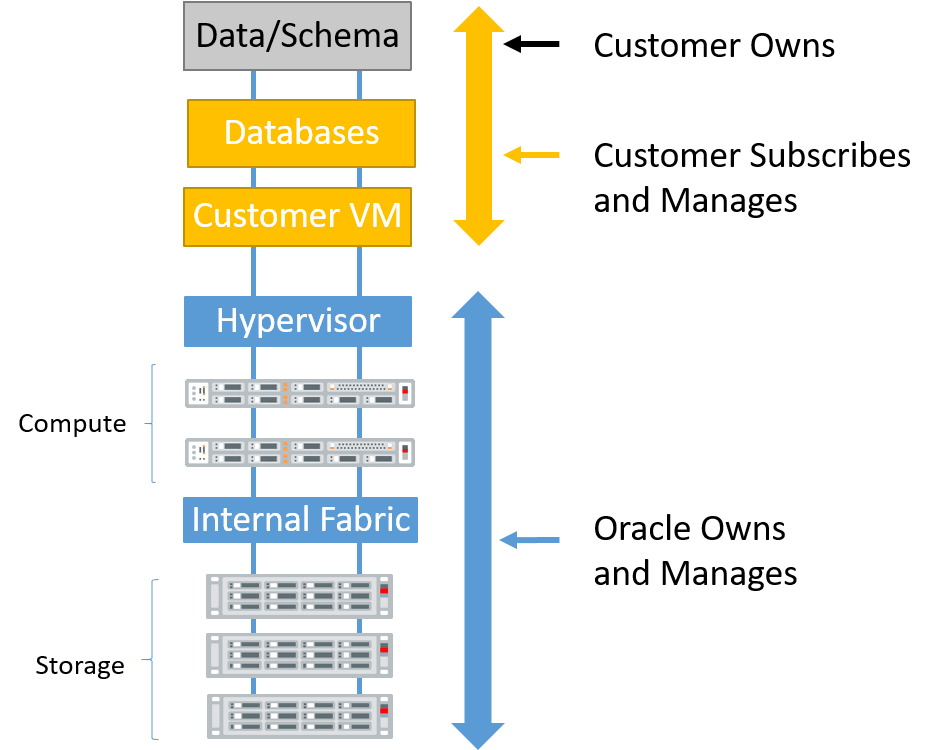
Oracle is responsible for the base OS and hardware. The customer is responsible for the Guest VM OS, Grid Infrastructure, and the database software maintenance.
Roles and Responsibilities for Exadata Cloud Infrastructure Software Maintenance
Oracle is responsible for the base OS and hardware. The customer is responsible for the Guest VM OS, Grid Infrastructure, and the database software maintenance.
Customer Responsibilities
Customer is responsible for the Guest VM OS, Grid Infrastructure, and the database software maintenance.
The customer owns everything inside the database: data schema, and encryption keys.
- Customer manages VMs and Databases using Cloud Automation (UI / APIs)
- Automation to create, delete, patch, backup, scale up/down, and so on
- Runs supported Oracle Database versions 19c and 26ai
- Customer controls access to customer VM
- Customer can install and manage additional software in customer VM
- Oracle staff are not authorized to access customer VM
Oracle Responsibilities
- Hypervisor, physical database and storage servers, storage network
- Patching, security scans, security updates
- Monitoring and maintenance
- Customer is not authorized to access Oracle infrastructure.
Parent topic: About Exadata Cloud Infrastructure
Licensing Considerations for Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure
Subscription to Exadata Cloud Infrastructure can include all of the required Oracle Database software licenses, or you can choose to bring Oracle Database software licenses that you already own to Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure.
If you choose to include Oracle Database software licenses in your Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure subscription, then the included licenses contain all of the features of Oracle Database Enterprise Edition, plus all of the database enterprise management packs, and all of the Enterprise Edition options, such as Oracle Database In-Memory and Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC). Exadata Cloud Infrastructure also comes with cloud-specific software tools that assist with administration tasks, such as backup, recovery, and patching.
Supported Database Edition and Versions for Exadata Cloud Infrastructure
Exadata Cloud Infrastructure databases require Enterprise Edition - Extreme Performance subscriptions or you can bring your own Oracle Enterprise Edition software licenses.
The Enterprise Edition - Extreme Performance provides all the features of Oracle Database Enterprise Edition, plus all the database enterprise management packs and all the Enterprise Edition options, such as Oracle Database In-Memory and Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC).
Exadata Cloud Infrastructure supports the following database versions:
- Oracle AI Database 26ai
- Oracle Database 19c
- Oracle Database 12c Release 2 (12.2) (Upgrade Support Required)
- Oracle Database 12c Release 1 (12.1) (Upgrade Support Required)
- Oracle Database 11g Release 2 (11.2) (Upgrade Support Required)
- Earlier database versions are supported on a 19c cloud VM cluster and can be created at anytime. Cloud VM clusters created with earlier Oracle Database versions will not automatically support Oracle Database 19c.
- For information on upgrading an existing database, see Upgrading Exadata Databases.
- To use Autonomous Recovery Service as a backup destination, your target database must have a minimum compatibility level of 19.0 (the
COMPATIBLEinitialization parameter must be set to 19.0.0 or higher).
For Oracle Database release and software support timelines, see Release Schedule of Current Database Releases (Doc ID 742060.1) in the My Oracle Support portal.
Subscription Types
Available subscription types.
- Pay As You Go
Pay As You Go (PAYG) pricing lets customers quickly provision services with no commitment, and they’re only charged for what they use. There’s no upfront commitment and no minimum service period. Any cloud infrastructure (IaaS) and platform (PaaS) services consumed are metered and billed based on that consumption. If, during the services period of your order, Oracle makes new IaaS and PaaS services available within your cloud services account, Oracle will notify you of any fees that would apply to their activation and use. For more details, see our complete price list.
- Annual Universal Credits
Oracle Annual Universal Credits enables customers to have the flexibility to use any Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and platform services at any time, in any region, to deliver faster time to market. Customers can commit to an amount of Oracle Annual Universal Credits that can be applied towards the future usage of eligible Oracle IaaS and PaaS cloud services. This payment option offers a significant savings across cloud services, combining cost reduction and a predictable monthly spend with a ramp up period as you onboard your workloads.
Metering Frequency and Per-Second Billing
Per-Second billing, minimums and limitations on billing.
For each Exadata Cloud Infrastructure instance you provision, you are billed for the infrastructure for a minimum of 48 hours, and then by the second after that. Each OCPU you add to the system is billed by the second, with a minimum usage period of 1 minute. If you terminate the cloud VM cluster and do not terminate the cloud Exadata infrastructure resource, billing will continue for the infrastructure resource.
Technical Architecture of Exadata Cloud Infrastructure Systems
Exadata Cloud Infrastructure systems integrate Oracle's Exadata Database Machine hardware with the networking resources needed to securely connect to your organization’s on-premise network and to other services in the Oracle cloud.
For a complete architectural overview of the components that make up an Exadata Cloud Infrastructure system, see Oracle Exadata Cloud Service (ExaCS) Technical Architecture. This interactive reference guides you through the key hardware and networking resources in the system, and provides technical specifications for the database (compute) and storage servers to help you plan for your deployment.
Scaling Options
Introduction to the Scaling option on Exadata Cloud Infrastructure.
Introduction to the Scaling option on Exadata Cloud Infrastructure.
Two kinds of scaling operations are supported for an Exadata Cloud Infrastructure:
- For X8M, X9M, and X11M systems, the flexible shape allows you to add additional database and storage servers to the cloud Exadata infrastructure resource as needed. See Overview of X8M, X9M, and X11M Scalable Exadata Infrastructure.
For more information on each type of scaling, see Scaling an Exadata Cloud Infrastructure Instance.
- Scaling CPU cores within an Exadata Cloud Infrastructure instance
If an Exadata Cloud Infrastructure instance requires more compute node processing power, you can scale up the number of enabled CPU cores (ECPUs for X11M) symmetrically across all the nodes in the system as follows: - Scaling X6, X7 and X8 Exadata Cloud Infrastructure Instances Configurations
Scaling an Exadata X6, X7, or X8 Exadata Cloud Infrastructure instance by moving to a shape with more capacity enables you meet the needs of your growing workload.
Related Topics
Scaling CPU cores within an Exadata Cloud Infrastructure instance
If an Exadata Cloud Infrastructure instance requires more compute node processing power, you can scale up the number of enabled CPU cores (ECPUs for X11M) symmetrically across all the nodes in the system as follows:
The options for each of the shapes are:
You can scale the infrastructure by adding DB servers or Storage Servers, up to the infrastructure limits. For more information on adding compute and storage resources to an X8M or X9M system enabled for MVM, see Scaling Exadata X8M or X9M Compute and Storage.
You can scale CPU cores (ECPUs for X11M) in multiples of the number of database servers currently provisioned for the cloud VM cluster. For example, if you have 6 database servers provisioned, you can add CPU cores in multiples of 6. In the case of X11M, if you have 6 database servers provisioned, you can add ECPUs in multiples of 24. At the time of provisioning, X8M, X9M, and X11M systems have as few as 2 database servers or up to 32 database servers. For more information on adding compute and storage resources to an X8M or X9M system, see Scaling Exadata X8M or X9M Compute and Storage (replace this text with "Scaling Exadata X8M, X9M, and X11M Compute and Storage")
All systems that are not X8M, X9M, or X11M are fixed shape systems. For a base system or an X7 or X8 quarter rack, you can scale in multiples of 2 across the 2 database compute nodes. For an X7 or X8 half rack, you can scale in multiples of 4 across the 4 database compute nodes. For an X7 or X8 full rack, you can scale in multiples of 8 across the 8 database compute nodes.
For non-metered service instances, you can temporarily modify the compute node processing power (bursting) or add compute node processing power on a more permanent basis. For a metered service instance, you can simply modify the number of enabled CPU cores.
You can provision an Exadata Cloud Infrastructure instance with zero CPU cores, or scale the service instance down to zero cores after you provision it. With zero cores, you are billed only for the infrastructure until you scale up the system. For detailed information about pricing, see Exadata Cloud Service Pricing.
OCPU (ECPUs for X11M) scaling activities are done online with no downtime.
For information on CPU cores per configuration, see Exadata Shape Configurations. To learn how to scale a system, see To scale CPU cores in an Exadata Cloud Infrastructure cloud VM cluster.
Scaling X6, X7 and X8 Exadata Cloud Infrastructure Instances Configurations
Scaling an Exadata X6, X7, or X8 Exadata Cloud Infrastructure instance by moving to a shape with more capacity enables you meet the needs of your growing workload.
This is useful when a database deployment requires:
- Processing power that is beyond the capacity of the current system configuration.
- Storage capacity that is beyond the capacity of the current system configuration.
- A performance boost that can be delivered by increasing the number of available compute nodes.
- A performance boost that can be delivered by increasing the number of available Exadata Storage Servers.
You can move your workloads to a larger fixed shape (X7 and X8 hardware shapes) or to the flexible X8M shape, which allows for easy expansion of compute and storage resources as your workloads grow.
To assist with moving your database deployments between Exadata Cloud Infrastructure instances, you can restore a backup to a different service instance with more capacity, create a Data Guard association for your database in a service instance with more capacity, and then perform a switchover so that your new standby database assumes the primary role. To start the process, contact Oracle and request a service limit increase so that you can provision the larger service instance needed by your database.
Parent topic: Scaling Options
System and Shape Configuration Options
Review the list of Exadata System Shapes
- Exadata Shape Configuration
This topic describes the available Exadata Cloud Infrastructure instance shapes in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
Exadata Shape Configuration
This topic describes the available Exadata Cloud Infrastructure instance shapes in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
Exadata X11M, X9M, and X8M shapes start with 2 database and 3 storage servers. Compute and/or storage servers can be added independently to these shapes up to a total of 32 DB servers and 64 storage servers. The initial minimum configuration for Exadata X6, X7, and X8 also starts with 2 database and 3 storage servers similar to the quarter rack shape. They are also offered in half and full rack shapes.
See the following sections for shape specifications:
- Exadata X11M
The values in the table that follows represent the specifications for an X11M Exadata Cloud Infrastructure with 2 database and 3 storage servers that has not been expanded. - Exadata X9M
The values in the table that follows represent the specifications for an X9M Exadata Cloud Infrastructure with 2 database and 3 storage servers that has not been expanded. - Exadata X8M
The values in the table that follows represent the specifications for an X8M cloud instance with 2 database and 3 storage servers that has not been expanded. - Exadata X8 Shapes
The values in the table that follows represent the specifications for an X8 cloud instance with fixed Quarter, Half, and Full Rack shapes. - Exadata X7 Shapes
The values in the table that follows represent the specifications for an X7 cloud instance with fixed Quarter, Half, and Full Rack shapes. - Exadata X6 Shapes
The values in the table that follows represent the specifications for an X6 cloud instance with fixed Quarter, Half, and Full Rack shapes. - Exadata Base System
An Exadata Base System is a fixed shape similar in size to a Quarter Rack with some differences in capacity.
Parent topic: System and Shape Configuration Options
Exadata X11M
The values in the table that follows represent the specifications for an X11M Exadata Cloud Infrastructure with 2 database and 3 storage servers that has not been expanded.
Independently add compute and/or storage servers up to a total of 32 database servers and 64 storage servers.
- A single database (DB) server contains 760 ECPUs and 1390 GB of memory.
- A single storage server contains 80 TB of usable disk storage capacity.
| Property | Minimum Configuration |
|---|---|
| Number of DB servers per System | 2 |
| Number of Storage Servers per System | 3 |
| Minimum (Default) Number of Enabled ECPUs | 0 |
| Total Usable ECPUs in DB Servers per System | 1520 |
| Total Memory Available for VMs (GB) | 2780 |
| Max Usable Local Storage Per DB Server (GB) | 2243 |
| Max Usable File System Size Per VM (GB) | 900 |
| VM Image size minimum and default (GB) | 244 |
| Max Number of VM Clusters per System | 8 |
| Max Number of VMs per DB server | 8 |
| Total Flash Capacity (TB) | 81.6 |
| Total Usable Disk Storage Capacity (TB) | 240 |
VM Image size minimum and default includes 60 GB for /u02.
A maximum of 8 VM Clusters can be created on a single infrastructure. For more information, see Estimating How Much Local Storage You Can Provision to Your VMs and Scaling Local Storage.
Parent topic: Exadata Shape Configuration
Exadata X9M
The values in the table that follows represent the specifications for an X9M Exadata Cloud Infrastructure with 2 database and 3 storage servers that has not been expanded.
Independently add compute and/or storage servers up to a total of 32 DB servers and 64 storage servers.
- A single DB server contains 126 usable cores and 1390 GB memory.
- A single storage server contains 63.6 TB of usable disk storage capacity.
| Property | Minimum Configuration |
|---|---|
| Number of DB servers per System | 2 |
| Number of Storage Servers per System | 3 |
| Minimum (Default) Number of Enabled CPU Cores | 0 |
| Total Usable Cores in DB Servers per System | 252 |
| Total Memory Available for VMs (GB) | 2780 |
| Max Usable Local Storage Per DB Server (GB) | 2243 |
| Max Usable File System Size Per VM (GB) | 900 |
| VM Image size minimum and default (GB) | 244 |
| Max Number of VM Clusters per System | 8 |
| Max Number of VMs per DB server | 8 |
| Total Flash Capacity (TB) | 76.8 |
| Total Usable Disk Storage Capacity (TB) | 190 |
VM Image size minimum and default includes 60 GB for /u02.
A maximum of 8 VM Clusters can be created on a single infrastructure. For more information, see Estimating How Much Local Storage You Can Provision on Your VMs and Scaling Local Storage.
Parent topic: Exadata Shape Configuration
Exadata X8M
The values in the table that follows represent the specifications for an X8M cloud instance with 2 database and 3 storage servers that has not been expanded.
Independently add compute and/or storage servers up to a total of 32 DB servers and 64 storage servers.
- A single DB server contains 50 usable cores and 1390 GB memory.
- A single storage server contains 49.9 TB of usable disk storage capacity.
| Property | Minimum Configuration |
|---|---|
| Number of DB servers per System | 2 |
| Number of Storage Servers per System | 3 |
| Minimum (Default) Number of Enabled CPU Cores | 0 |
| Total Usable Cores in DB Servers per System | 100 |
| Total Memory Available for VMs (GB) | 2780 |
| Max Usable Local Storage Per DB Server (GB) | 2243 |
| Max Usable File System Size Per VM (GB) | 900 |
| VM Image size minimum and default (GB) | 244 |
| Max Number of VM Clusters per System | 8 |
| Max Number of VMs per DB server | 8 |
| Total Flash Capacity (TB) | 76.8 |
| Total Usable Disk Storage Capacity (TB) | 149 |
VM Image size minimum and default includes 60 GB for /u02.
A maximum of 8 VM Clusters can be created on a single infrastructure. For more information, see Estimating How Much Local Storage You Can Provision on Your VMs and Scaling Local Storage.
Parent topic: Exadata Shape Configuration
Exadata X8 Shapes
The values in the table that follows represent the specifications for an X8 cloud instance with fixed Quarter, Half, and Full Rack shapes.
| Property | Quarter Rack | Half Rack | Full Rack |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shape Name | Exadata.Quarter3.100 | Exadata.Half3.200 | Exadata.Full3.400 |
| Number of DB servers per System | 2 | 4 | 8 |
| Number of Storage Servers per System | 3 | 6 | 12 |
| Minimum Number (Default) of Enabled CPU Cores | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total Usable Cores in DB Servers per System | 100 | 200 | 400 |
| Total Memory Available (GB) | 1440 | 2880 | 5760 |
| Max Usable Local Storage (GB) | 700 | 700 | 700 |
| Total Flash Capacity (TB) | 76.8 | 179.2 | 358.4 |
| Total Usable Disk Storage Capacity (TB) | 149 | 299 | 598 |
Parent topic: Exadata Shape Configuration
Exadata X7 Shapes
The values in the table that follows represent the specifications for an X7 cloud instance with fixed Quarter, Half, and Full Rack shapes.
| Property | Quarter Rack | Half Rack | Full Rack |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shape Name | Exadata.Quarter2.92 | Exadata.Half2.184 | Exadata.Full2.368 |
| Number of DB servers per System | 2 | 4 | 8 |
| Number of Storage Servers per System | 3 | 6 | 12 |
| Minimum Number (Default) of Enabled CPU Cores | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total Usable Cores in DB Servers per System | 92 | 184 | 368 |
| Total Memory Available (GB) | 1440 | 2880 | 5760 |
| Max Usable Local Storage (GB) | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| Total Flash Capacity (TB) | 76.8 | 153.6 | 307.2 |
| Total Usable Disk Storage Capacity (TB) | 106 | 212 | 424 |
Parent topic: Exadata Shape Configuration
Exadata X6 Shapes
The values in the table that follows represent the specifications for an X6 cloud instance with fixed Quarter, Half, and Full Rack shapes.
| Property | Quarter Rack | Half Rack | Full Rack |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shape Name | Exadata.Quarter1.84 | Exadata.Half1.168 | Exadata.Full1.336 |
| Number of DB servers per System | 2 | 4 | 8 |
| Number of Storage Servers per System | 3 | 6 | 12 |
| Minimum Number (Default) of Enabled CPU Cores | 22 | 44 | 88 |
| Total Usable Cores in DB Servers per System | 84 | 168 | 336 |
| Total Memory Available (GB) | 1440 | 2880 | 5760 |
| Max Usable Local Storage (GB) | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| Total Flash Capacity (TB) | 38.4 | 76.8 | 153.6 |
| Total Usable Disk Storage Capacity (TB) | 73 | 168 | 336 |
Exadata X6 shapes must be provisioned using the License Included option. Bring-Your-Own-License (BYOL) is not supported with the X6 shapes.
Parent topic: Exadata Shape Configuration
Exadata Base System
An Exadata Base System is a fixed shape similar in size to a Quarter Rack with some differences in capacity.
| Property | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Number of DB servers per System | 2 |
| Number of Storage Servers per System | 3 |
| Minimum Number of Enabled CPU Cores | 0 |
| Total Usable Cores in DB Servers per System | 48 |
| Total Memory Available (GB) | 720 |
| Max Usable Local Storage (GB) | 900 |
| Total Flash Capacity (TB) | 38.4 |
| Total Usable Disk Storage Capacity (TB) | 73 |
For information on provisioning an Exadata Cloud Infrastructure instance, see Creating an Exadata Cloud Infrastructure Instance.
Parent topic: Exadata Shape Configuration