Examples of Semantic Clustering
The nlp command can be used to extract keywords from a
string field, or to cluster records based on these extracted keywords. Keyword
extraction can be controlled using a custom NLP dictionary. If no dictionary is
provided, the default Oracle-defined dictionary is used.
Topics:
For more information on semantic clustering, see Semantic Clustering.
Cluster Kernel Errors in Linux Syslog Logs
The following query clusters Kernel messages in Linux Syslog Logs:
'Log Source' = 'Linux Syslog Logs' and kernel
| link cluster()
| where 'Potential Issue' = '1'
| nlp table = 'iSCSI Errors' cluster('Cluster Sample') as 'Cluster ID',
keywords('Cluster Sample') as Summary
| sort 'Cluster ID'In the above query:
-
link cluster()runs the traditional cluster and returns aCluster Samplefield. -
nlp cluster('Cluster Sample')processes eachCluster Sampleand assigns a Cluster ID. Messages that have similar meaning would get the same Cluster ID. -
keywords('Cluster Sample')extracts the keywords used in clustering. This is returned in theSummaryfield.
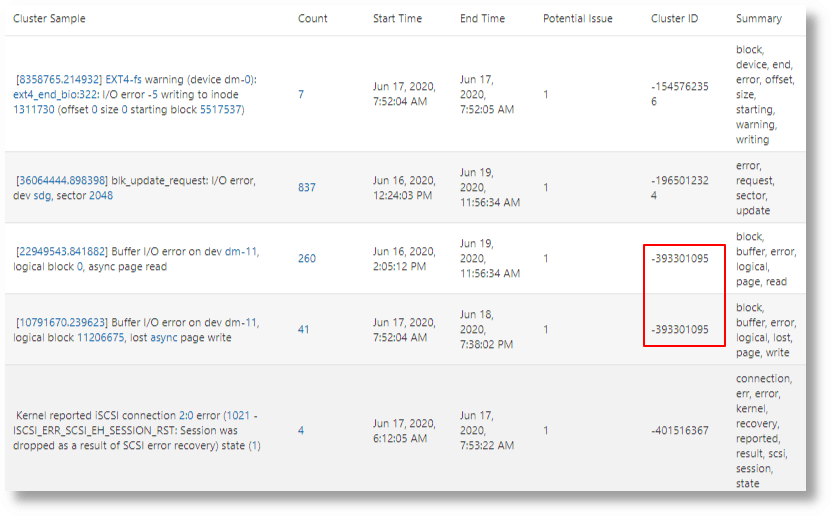
The following image shows the link results returned:
-
The first and second rows are not similar, and hence get different cluster IDs.
-
The third and fourth rows have similarity in the Cluster Sample. This can be seen in the overlap of keywords extracted in the
Summaryfield. -
By default, a 70% overlap is required to form a cluster. This can be overridden using the
similarityparameter to cluster. -
The Cluster ID generated is deterministic. Thus, the Cluster ID can be used as a shortcut for the list of keywords shown in the Summary column.
Use similarity
to Control the Number of Clusters
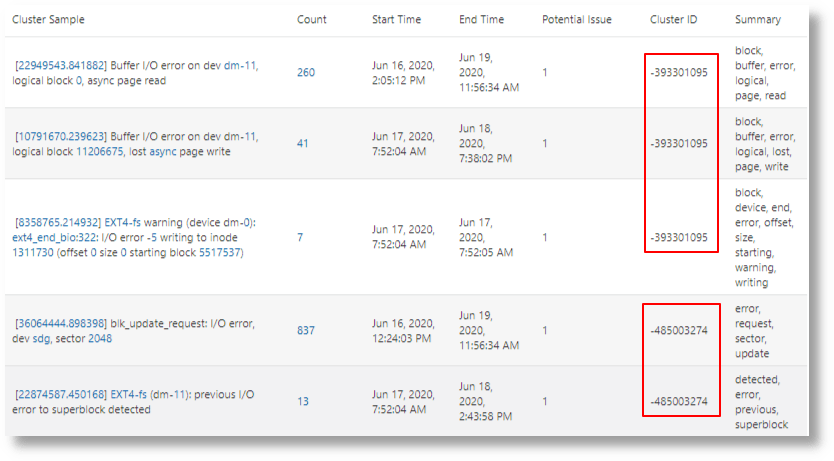
Running cluster using the default dictionary and a lower similarity threshold would produce fewer clusters:
'Log Source' = 'Linux Syslog Logs' and kernel
| link cluster()
| where 'Potential Issue' = '1'
| nlp similarity=0.2 cluster('Cluster Sample') as 'Cluster ID',
keywords('Cluster Sample') as Summary
| sort 'Cluster ID'This merged some of the rows into the existing clusters, as well as reduced the number of clusters:
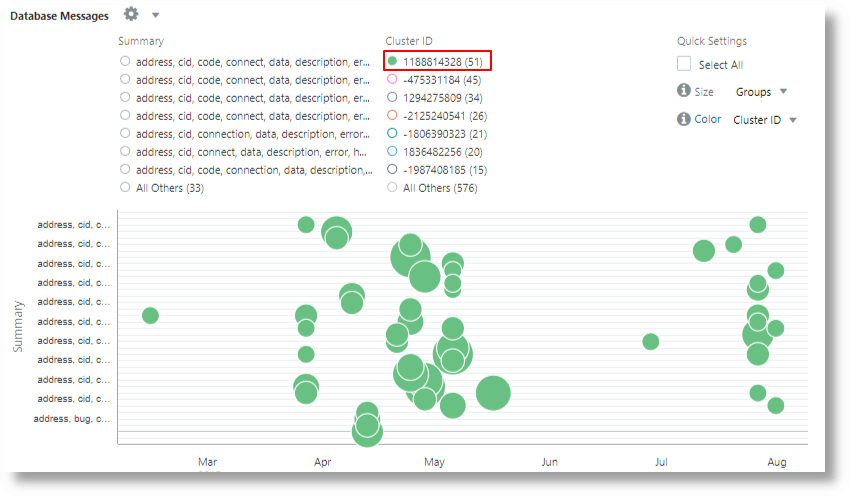
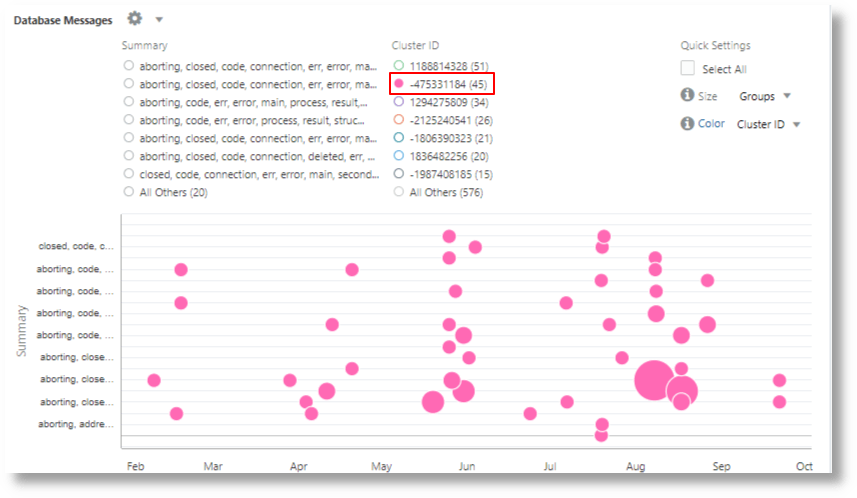
Cluster the Database Alert Logs
The following query shows an example of semantically clustering Database Alert Logs:
'Log Source' = 'Database Alert Logs'
| link cluster()
| nlp cluster('Cluster Sample') as 'Cluster ID',
keywords('Cluster Sample') as Summary
| where Summary != null
| classify 'Start Time', Summary, 'Cluster ID' as 'Database Messages'