Disable a Cross-Region Standby Database
Disabling a cross-region Autonomous Data Guard standby database terminates the standby database. If you later add a cross-region Autonomous Data Guard standby, the system creates a new cross-region standby database.
You have two options to disable a cross-region Autonomous Data Guard standby:
You can update the cross-region disaster recovery type to use Backup-Based Disaster Recovery. This terminates the cross-region Autonomous Data Guard standby database and adds a cross-region backup copy peer.
You can terminate the cross-region Standby database.
- Update Cross-Region Standby to Use Backup-Based Disaster Recovery
You can update the disaster recovery type from cross-region Autonomous Data Guard standby database to cross-region Backup-Based Disaster Recovery. This terminates the cross-region Autonomous Data Guard standby database. - Terminate a Cross-Region Standby Database
Describes the steps to terminate a cross-region standby database. - Verify Cross-Region Autonomous Data Guard is Disabled
Describes the steps to verify that an Autonomous Data Guard cross-region standby is disabled.
Update Cross-Region Standby to Use Backup-Based Disaster Recovery
You can update the disaster recovery type from cross-region Autonomous Data Guard standby database to cross-region Backup-Based Disaster Recovery. This terminates the cross-region Autonomous Data Guard standby database.
Perform the following prerequisite steps as necessary:
-
Open the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console by clicking the
 next to Cloud.
next to Cloud.
-
From the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure left navigation menu click Oracle Database and then click Autonomous AI Database.
-
On the Autonomous AI Database page, select your Autonomous AI Database from the links under the Display name column.
To change your disaster recovery type to use a cross-region backup-copy peer:
Autonomous AI Database generates a Change Disaster Recovery Configuration work request. To view the request, on the Autonomous AI Database details page select the Work requests tab.
Parent topic: Disable a Cross-Region Standby Database
Terminate a Cross-Region Standby Database
Describes the steps to terminate a cross-region standby database.
Perform the following prerequisite steps as necessary:
-
Open the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console by clicking the
 next to Cloud.
next to Cloud.
-
From the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure left navigation menu click Oracle Database and then click Autonomous AI Database.
-
On the Autonomous AI Database page, select your Autonomous AI Database from the links under the Display name column.
To terminate a cross-region standby database:
If there is a local Autonomous Data Guard standby database, terminating the cross-region standby does not change the local disaster recovery option.
Note the following when your disaster recovery option includes a cross-region disaster recovery peer:
-
A cross-region disaster recovery peer cannot be terminated from the primary database.
-
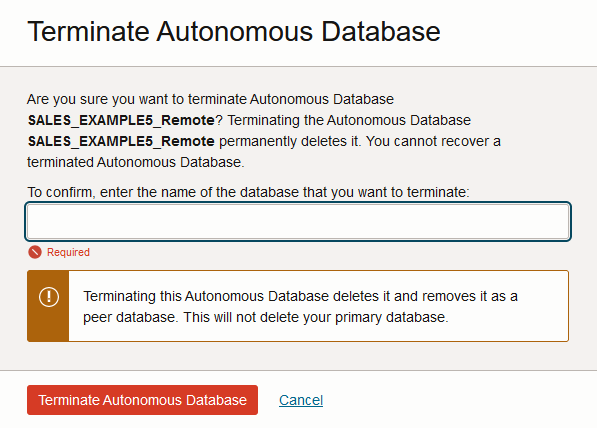
You must terminate all cross-region disaster recovery peers before you terminate the primary database. If you attempt to terminate the primary when there is a cross-region disaster recovery peer, the system shows the following message:
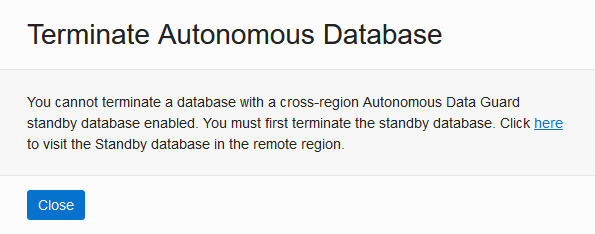
Description of the illustration adb_data_guard_terminate_primary.pngIn this case, first terminate the cross-region (remote) peers and then you can terminate the Primary role database.
After the cross-region disaster recovery peers are terminated, then terminate the Primary database. See Terminate an Autonomous AI Database Instance for more information.
Parent topic: Disable a Cross-Region Standby Database
Verify Cross-Region Autonomous Data Guard is Disabled
Describes the steps to verify that an Autonomous Data Guard cross-region standby is disabled.
To verify that a cross-region Autonomous Data Guard standby database is disabled:
- On the primary database, on the Autonomous AI Database Details page select the Disaster recovery tab.
- Verify that either the disaster recovery type is changed to backup copy or the cross-region Autonomous Data Guard standby is terminated.
-
If you updated the disaster recovery type to use cross-region backup based disaster recovery, verify that the remote peer autonomous database DR Type shows backup copy.
-
If you manually terminated standby database, verify that the cross-region standby count is 0 (that is there is no remote peer).
Parent topic: Disable a Cross-Region Standby Database