Access Oracle APEX, Oracle REST Data Services, and Built-in Database Tools Using a Vanity URL
By default, access to Oracle APEX apps, REST endpoints and built-in database tools on Autonomous AI Database is through the oraclecloudapps.com domain name. You may optionally configure a vanity URL (ie. a custom domain) that is more relevant for your organization or project.
For this, you must first acquire your desired domain name and matching SSL certificate from a vendor of your choice.
- Enable a Vanity URL on your Elastic Pool Member Database
With a registered domain name and certificate available, for a database in an elastic pool, you can easily enable a vanity URL on your Autonomous AI Database and configure a vanity URL custom domain for your Autonomous AI Database instance using an API Gateway. - Enable a Vanity URL on your Non-Elastic Pool Database using a Reverse Proxy
For a database that is not part of an elastic pool, you may manually deploy an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Load Balancer in your Virtual Cloud Network (VCN) using your Autonomous AI Database as the backend.
Enable a Vanity URL on your Elastic Pool Member Database
With a registered domain name and certificate available, for a database in an elastic pool, you can easily enable a vanity URL on your Autonomous AI Database and configure a vanity URL custom domain for your Autonomous AI Database instance using an API Gateway.
- Vanity URLs are supported by OCI API gateways that use HTTP endpoints, but not by TCP-based endpoints such as MongoDB and SQLNET.
- The Oracle Machine Language (OML) tool does not support vanity URL.
- Register your API Gateway with your DNS
This chapter highlights the importance of setting up Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Domain Name System (DNS) in configuring a vanity URL. - Enable Resource Principal to Access Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Resources
Perform the following steps to enable resource principal on Autonomous AI Database. This allows the database to authenticate and access OCI resources securely. - IAM Policy to Setup a Vanity URL
Before you configure a vanity URL for your Autonomous AI Database instance on your Elastic Pool Member Database you must grant permissions to database to manage the OCI API Gateway deployments - Enable a Vanity URL on your Elastic Pool Member Database
Follow these instructions to configure a vanity URL for your Autonomous AI Database instance using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Service Console.
Register your API Gateway with your DNS
This chapter highlights the importance of setting up Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Domain Name System (DNS) in configuring a vanity URL.
Configuring the DNS to point to an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) API Gateway is necessary to enable a vanity URL because DNS is the system that translates the user-friendly custom domain name (e.g., api.mycompany.com) into the IP address of the actual OCI API Gateway endpoint. Without configuring DNS, the custom domain won't resolve to the OCI API Gateway's public IP, and users would not be able to reach your OCI APIs using the vanity URL.
- Domain ownership and verification:
A vanity domain requires proof of ownership. The domain must be registered with an authorized domain registrar, and you must have administrative control to manage its DNS records. This ensures only legitimate owners can map their custom domain (for example,
examplehost.com) to the OCI API Gateway endpoint. - TLS certificates for HTTPS:
As OCI API Gateways are secured with Transport Layer Security (TLS), a TLS certificate is mandatory. If you use Oracle’s default (auto-generated) domain, Oracle automatically provisions and maintains a certificate. However, when using a custom domain, you must provide your own TLS certificate obtained from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). This certificate binds your vanity domain to the gateway, enabling encrypted communication and ensuring client trust.
There are two approaches:-
Use an Oracle-managed certificate via the OCI Certificates service (self-issued or imported from a CA).
-
Upload your own custom certificate, along with the private key and any intermediate certificates.
-
-
DNS record configuration:
Once the OCI API Gateway and TLS certificate are set up, you must configure DNS so the custom domain resolves to the gateway’s public endpoint.
Without this process, inbound requests to your custom domain would not reach the gateway.
The DNS is like a bridge between your vanity domain and the underlying OCI API Gateway infrastructure. For your vanity URL to be reachable and functional, you must point your DNS records to the API Gateway.
Steps to configure DNS for OCI API Gateway
To configure DNS to point to an OCI API Gateway, you must perform the following steps that involve domain ownership, TLS certificates and DNS record configuration.
- You must own a registered domain name (whether managed in OCI DNS or an external DNS provider) before configuration begins.
- You must procure a TLS certificate for your custom domain either from a third-party Certificate Authority (CA) or via OCI Certificates Service.
- Create and Upload a Custom TLS Certificate:
-
Generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) for your domain, including your fully qualified domain name (FQDN).
- Use either the OCI Certificates Service or a third-party CA to issue the certificate.
- Import this certificate and private key into OCI as a Certificate resource.
Refer to Setting Up Custom Domains and TLS Certificates for more details.
-
- Create an API Gateway in OCI:
-
Navigate to Developer Services > API Gateway in OCI Console.
- Create a gateway with your TLS certificates at appropriate public Subnet of VCN.
After creation, keep a note of the
API Gateway OCID IDwhich OCI generates automatically.Refer to Creating an API Gateway for more details.
-
- Configure DNS Records for Your Domain:
- Go to your DNS management system (either OCI DNS service or an external DNS provider such as Route 53) to configure your custom DNS mapping to OCI API Gateway public IP address.
This ensures incoming traffic for your custom domain resolves to your OCI API Gateway Public IP address.
After DNS propagation, you can then access the vanity URL (https://examplehost.com) and confirm it routes to your OCI API Gateway Public IP address.
You can also configure a vanity URL for Autonomous AI Database from the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Service Console for Elastic Pool users.
Parent topic: Enable a Vanity URL on your Elastic Pool Member Database
Enable Resource Principal to Access Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Resources
Perform the following steps to enable resource principal on Autonomous AI Database. This allows the database to authenticate and access OCI resources securely.
As a prerequisite, configure dynamic groups and policies. See Perform Prerequisites to Use Resource Principal with Autonomous AI Database for more information.
To enable a resource principal on Autonomous AI Database:
Enabling the resource principal on an Autonomous AI Database instance is one-time operation. You do not need to enable the
resource principal again, unless you run DBMS_CLOUD_ADMIN.DISABLE_RESOURCE_PRINCIPAL to
disable the resource principal.
Parent topic: Enable a Vanity URL on your Elastic Pool Member Database
IAM Policy to Setup a Vanity URL
Before you configure a vanity URL for your Autonomous AI Database instance on your Elastic Pool Member Database you must grant permissions to database to manage the OCI API Gateway deployments
- Open the navigation menu and click Identity & Security. Under Identity, click Policies.
- Click Create Policy.
- In the Create Policy window, enter a name (for example,
IntegrationGroupPolicy) and a description. - In the Policy Builder, select Show manual editor and enter the required policy statements.
The typical Syntax to allow a group to manage API Gateway deployments is:
-
Allow dynamic-group id <
dynamic group ocid> to manage api-deployments in compartment <compartment name> -
Allow dynamic-group id <
dynamic group ocid> to use api-gateways in compartment <compartment name>
Example:- Allow dynamic-group id
ocid1.dynamicgroup.oc1..aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa1111ex3aztuwucyjiqoclhpuflmlncmkwtqsjwlmmqto manage api-deployments in compartmentadwtoolsqa - Allow dynamic-group id
ocid1.dynamicgroup.oc1..aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa1111ex3aztuwucyjiqoclhpuflmlncmkwtqsjwlmmqto use api-gateways in compartmentadwtoolsqa
This policy statement allows the
ocid1.dynamicgroup.oc1..aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa1111ex3aztuwucyjiqoclhpuflmlncmkwtqsjwlmmqgroup in the admin domain to manage and use OCI API Gateway Deployments in compartmentadwtoolsqa.Note
- When defining policy statements, you can specify either verbs (as used in these steps) or permissions (typically used by power users).
-
To learn more about policies, see:
How Policies Work and Policy Reference in the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure documentation.
-
-
Review and create the policy.
The policy statements are validated and syntax errors are displayed.
Parent topic: Enable a Vanity URL on your Elastic Pool Member Database
Enable a Vanity URL on your Elastic Pool Member Database
Follow these instructions to configure a vanity URL for your Autonomous AI Database instance using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Service Console.
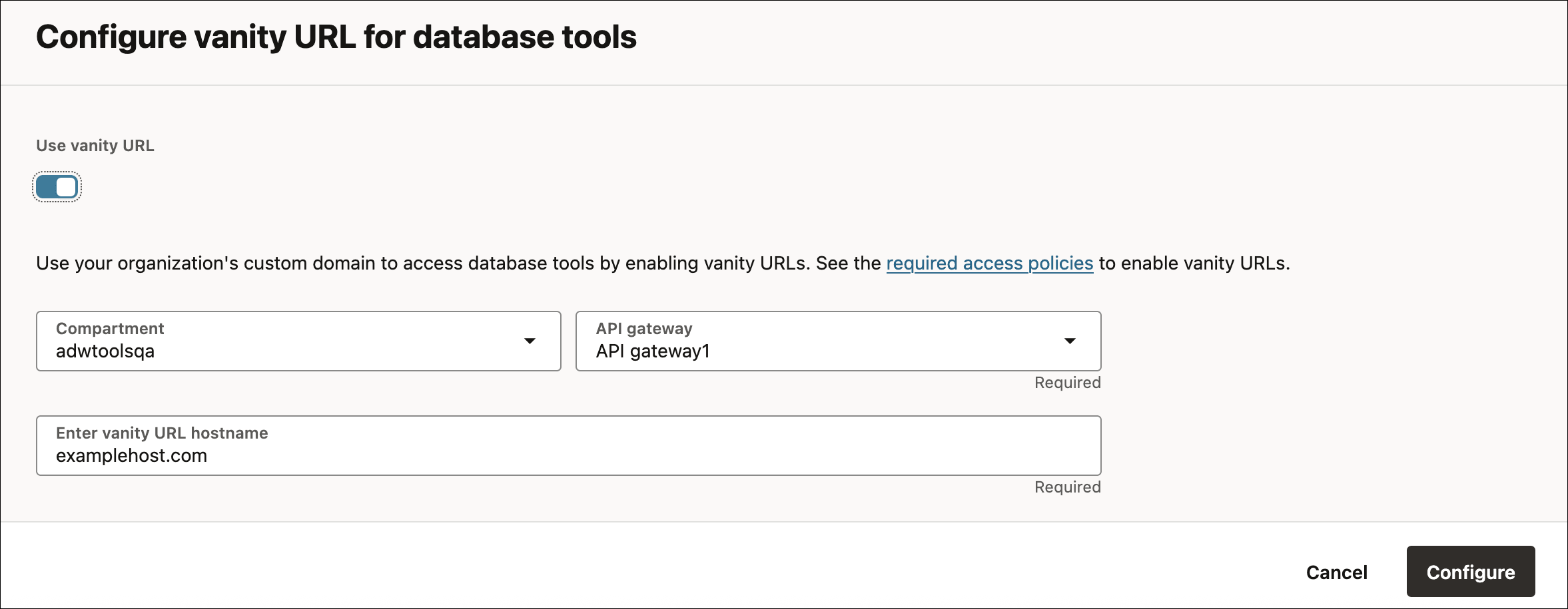
- On the Autonomous AI Database Details page, from the More actions drop-down list, select Enable vanity URL.
- On the Configure vanity URL for database tools dialog, select Use vanity URL.
- Select the Compartment of your OCI API Gateway.
- Select the API Gateway from the list of OCI API Gateway names you have access to.
- Specify the fully qualified custom domain name that should appear in the URL and is registered with DNS.
For example, enter
examplehost.com.Click Configure.
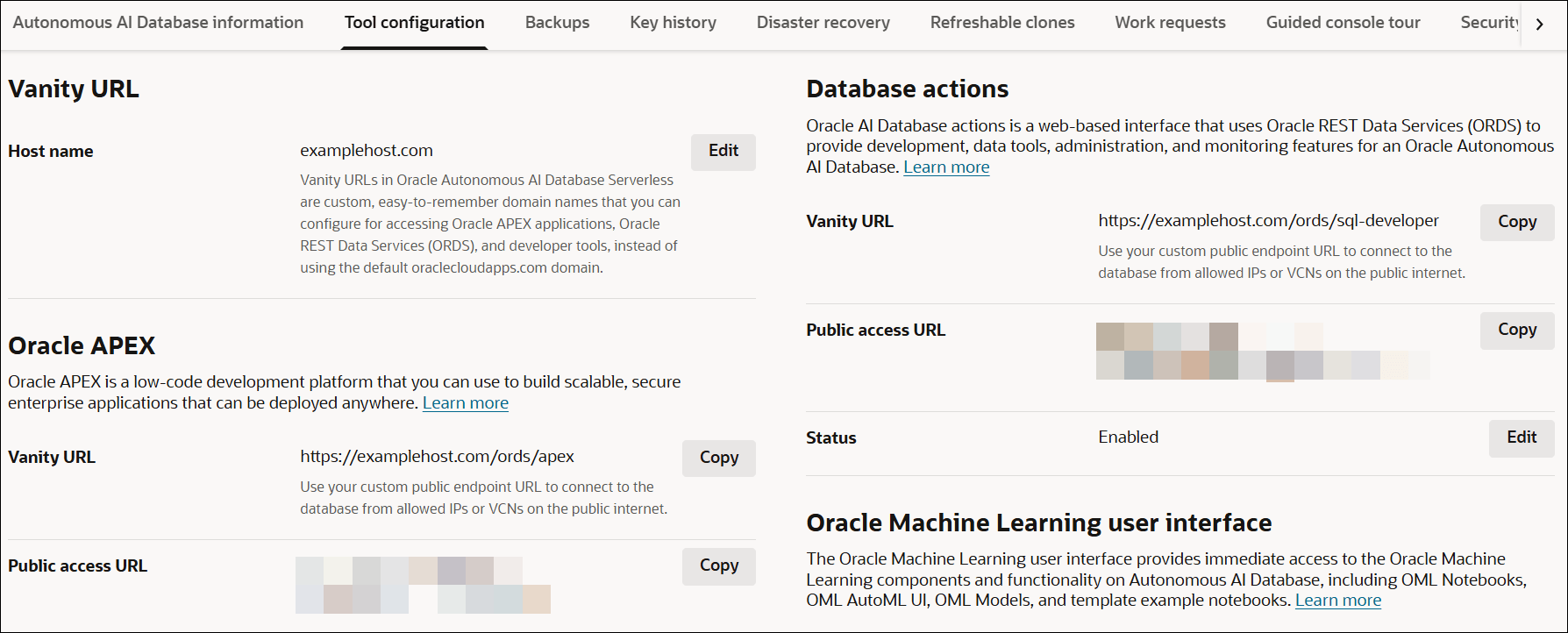
After successful configuration, the Tool Configuration tab on the Autonomous AI Database Details page displays a new field named Vanity URL, along with additional Vanity URL fields under Oracle APEX and Database Actions.
You will be able to access end-user applications and developer tools such as Oracle APEX and Database Actions using your custom domain name or Public/Private access URL based on your database network access.
Parent topic: Enable a Vanity URL on your Elastic Pool Member Database
Enable a Vanity URL on your Non-Elastic Pool Database using a Reverse Proxy
For a database that is not part of an elastic pool, you may manually deploy an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Load Balancer in your Virtual Cloud Network (VCN) using your Autonomous AI Database as the backend.
Your Autonomous AI Database instance must be configured with a private endpoint in the same VCN. See Configure Network Access with Private Endpoints for more information.