Deploy the APM Java Agent
On successfully provisioning the APM Java agent, you can deploy the APM Java agent.
To deploy the APM Java agent on any Java application, you need to add the
-javaagent parameter to the JVM startup script. Depending on the
Java environment, an application server or a microservice, users may have shell or bat
startup scripts, or another way to execute the Java command line.
See below examples on how to deploy the APM Java agent on the following Java applications:
Oracle WebLogic Server
Here's information on how to deploy the APM Java agent on the Oracle WebLogic Server.
- Set a variable to point to your application server destination directory. This is
the directory in which the APM Java agent is provisioned.
Set the
$DOMAIN_HOMEvariable to point to the Oracle WebLogic Server Domain directory and confirm that the APM Java agent was provisioned in the same destination directory before you perform the next step.Application Server Destination Directory Variable Information Oracle WebLogic Server Set the $DOMAIN_HOMEvariable to point to the Oracle WebLogic Server Domain.export DOMAIN_HOME=<Oracle WebLogic Server Domain> - Make a backup copy of the
startWebLogic.shfile:cd $DOMAIN_HOME/bin cp startWebLogic.sh startWebLogic.sh.orig - Use a text editor and edit the original
startWebLogic.shscript and add the-javaagentoption.- If you're deploying the APM Java agent on the Oracle WebLogic
Administration Server and Managed Servers, then add the following
-javaagentoption to the set ofJAVA_OPTIONS, after thesetDomainEnv.shcall:JAVA_OPTIONS="${JAVA_OPTIONS} -javaagent:$DOMAIN_HOME/oracle-apm-agent/bootstrap/ApmAgent.jar" - If you're deploying the APM Java agent on Managed Servers only, then add the following
-javaagentoption to the set ofJAVA_OPTIONSwithin anifstatement after thesetDomainEnv.shcall:if [ "$SERVER_NAME" != "AdminServer" ] ; then set JAVA_OPTIONS="${JAVA_OPTIONS} -javaagent:$DOMAIN_HOME/oracle-apm-agent/bootstrap/ApmAgent.jar" fi
- If you're deploying the APM Java agent on the Oracle WebLogic
Administration Server and Managed Servers, then add the following
- Stop and restart the Oracle WebLogic Server:
cd $DOMAIN_HOME/bin ./stopWebLogic.sh cd .. nohup ./startWebLogic.sh >& startup.log &If you have Managed Servers, stop and restart them too:
cd $DOMAIN_HOME/bin ./stopManagedWebLogic.sh {SERVER_NAME} {ADMIN_URL} {USER_NAME} {PASSWORD} nohup ./startManagedWebLogic.sh {SERVER_NAME} {ADMIN_URL} >& {SERVER_NAME}.log &Note
Notice that the$DOMAIN_HOMEversion ofstartWebLogic.shis used, even though you edited the$DOMAIN_HOME/binversion. Invoking the command from one level higher (from$DOMAIN_HOME) invokes the command from a lower level (from$DOMAIN_HOME/bin). However, thestopWebLogic.shcommand will be called from the$DOMAIN_HOME/bindirectory.
After the APM Java agent is successfully deployed, the Oracle APM
Agent: Initialized AgentInstance message is displayed in the server startup
log.
Apache Tomcat Server
Here's information on how to deploy the APM Java agent on the Apache Tomcat Server.
- Set a variable to point to your application server destination directory. This is
the directory in which the APM Java agent is provisioned.
Set the
$CATALINA_HOMEvariable to point to the Apache Tomcat Server destination directory and confirm that the APM Java agent was provisioned in the same destination directory before you perform the next step.Application Server Destination Directory Variable Information Apache Tomcat Server Set the $CATALINA_HOMEvariable to point to the Apache Tomcat Server destination directory.- If you're using a Bash
shell:
export CATALINA_HOME=<Apache Tomcat Server destination directory> - If you're using a C
shell:
setenv CATALINA_HOME "<Apache Tomcat Server destination directory>"
- If you're using a Bash
shell:
- Make a backup copy of the
catalina.shfile.$ cd $CATALINA_HOME/bin $ cp catalina.sh catalina.sh.orig - Use a text editor and edit the original
catalina.shfile and add the following-javaagentoption toCATALINA_OPTS. Make the change outside of anyifstatements or code blocks that may not be executed during server startup. This will ensure that the-javaagentflag is always added to the server startup options.CATALINA_OPTS="${CATALINA_OPTS} -javaagent:$CATALINA_HOME/oracle-apm-agent/bootstrap/ApmAgent.jar" - Stop and restart the Apache Tomcat
Server:
$ cd $CATALINA_HOME/bin $ ./shutdown.sh $ ./startup.sh
After the APM Java agent is successfully deployed, the Oracle APM
Agent: Initialized AgentInstance message is displayed in the server startup
log.
For more information, see Install an APM Java Agent on a Tomcat Application Server Tutorial.
Jetty Server
Here's information on how to deploy the APM Java agent on the Jetty Server.
- Set a variable to point to your application server destination
directory. This is the directory in which the APM Java agent is provisioned.
Set the
JETTY_HOMEvariable to point to the Jetty Server destination directory (where the Jetty software was extracted) and confirm that the APM Java agent was provisioned in the same destination directory before you perform the next step. - Start the Jetty server.
java -javaagent:/<Destination_Directory>/oracle-apm-agent/bootstrap/ApmAgent.jar -jar $JETTY_HOME/start.jar
After the APM Java agent is successfully deployed, the Oracle APM
Agent: Initialized AgentInstance message is displayed in the server startup
log.
Spring Boot
Here's information on how to deploy an APM Java agent on a Spring Boot microservice running embedded Apache Tomcat.
application.properties file to enable
Apache Tomcat
Mbeans:spring.jmx.enabled=true
server.tomcat.mbeanregistry.enabled=trueAlternatively, add the above properties: spring.jmx.enabled and
server.tomcat.mbeanregistry.enabled as system properties on the
command line.
-javaagent
option to the startup script of your microservice. Note that <Destination
Directory> denotes the directory in which you provisioned the
agent.java -javaagent:<Destination Directory>/oracle-apm-agent/bootstrap/ApmAgent.jar -jar target/<microservice.jar>After the APM Java agent is successfully deployed, the Oracle APM
Agent: Initialized AgentInstance message is displayed in the microservice
startup log.
JBoss Server
Here's information on how to deploy the APM Java agent on the JBoss Server.
The below instructions are applicable for JBoss EAP and Wildfly.
- Set a variable to point to your application server destination
directory. This is the directory in which the APM Java agent is provisioned.
Set the
$JBOSS_HOMEvariable to point to the JBoss Server destination directory and confirm that the APM Java agent was provisioned in the same destination directory before you perform the next step.Application Server Destination Directory Variable Information JBoss Server Set the
$JBOSS_HOMEvariable to point to the JBoss Server destination directory.- If you're using a Bash
shell:
export JBOSS_HOME=<JBoss Server destination directory> - If you're using a C shell:
setenv JBOSS_HOME "<JBoss Server destination directory>"
- If you're using a Bash
shell:
- Make a backup copy of the
standalone.conffile:cd $JBOSS_HOME/bin cp standalone.conf standalone.conf.orig - Use a text editor and edit the original
standalone.conffile and add the following Java options toJAVA_OPTS. Make the change outside of anyifstatements or code blocks that may not be executed during server startup.- Add
-javaagentoption toJAVA_OPTS.JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -javaagent:$JBOSS_HOME/oracle-apm-agent/bootstrap/ApmAgent.jar" - Edit Java property
jboss.modules.system.pkgsto include"com.oracle.apm".For example:
JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Djboss.modules.system.pkgs=org.jboss.byteman,org.jboss.logmanager,com.oracle.apm"Note
Each environment is different. The Jboss server's property may include different packages from what are shown in the above example.
- Add
- Stop and restart the JBoss
Server:
cd $JBOSS_HOME/bin ./jboss-cli.sh -c :shutdown nohup ./standalone.sh -b 0.0.0.0&> startup.log &
After the APM Java agent is successfully deployed, the Oracle APM
Agent: Initialized AgentInstance message is displayed in the server startup
log.
Docker and Kubernetes
Here's information on how to deploy an APM Java agent in a Docker container and Oracle Container Engine for Kubernetes (OKE).
Deploy APM Java Agent into Docker Container Image
Here's information on how to deploy an APM Java agent into a Docker container image and Oracle Container Engine for Kubernetes (OKE).
Figure 3-1 Deploy APM Java Agent into Docker Container Image
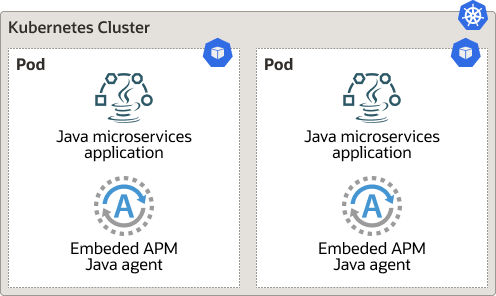
Recommendation:
Use this option when it's feasible to make changes to the Docker container image.
For example, if you may need to change the APM agent configuration, you are able to make changes to the Docker image.
To deploy the APM Java agent, follow the below steps:
- Before proceeding, confirm you have completed the prerequisites and provisioned the APM Java agent.
Note
When provisioning the APM Java agent, it's recommended to provision it in any location of your local machine and then copy it to a Docker image. - Modify your
Dockerfileto copy the APM Java agent to a Docker image:COPY <DESTINATION_DIRECTORY>/oracle-apm-agent <Docker_Image_Directory>/oracle-apm-agent/Note that
<DESTINATION_DIRECTORY>denotes the location on your local machine where you provisioned the APM Java agent and<Docker_Image_Directory>denotes the directory in the Docker image to which you're copying the APM Java agent. The<Docker_Image_Directory>could also be the application server destination directory in Docker, for example,$DOMAIN_HOME, if you're working with Oracle WebLogic Server. - Add the following
-javaagentoption to the startup script of your application server:java -javaagent:<Docker_Image_Directory>/oracle-apm-agent/bootstrap/ApmAgent.jar -jar target/<appserver.jar> - Build a new Docker image with the built-in APM Java agent and the modified startup script, and push the image to the registry.
If you use Kubernetes to manage your Docker containers, then update your Kubernetes configuration to use the new Docker image, and restart the Kubernetes pod.
Also, you can set additional dimensions to be reported from the Kubernetes pod using the Downward API, by copying the following environment and volume settings in the deployment specification (yaml file) of the Kubernetes pod. For information on the Downward API, see The Downward API in Kubernetes documentation.
Environment Settings
spec:
containers:
- name: <container-name>
image: image: <your-registry>/<your-docker-image>:latest
env:
- name: APM_ATTRIBUTES_K8S_POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: APM_ATTRIBUTES_K8S_NAMESPACE_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
- name: APM_ATTRIBUTES_K8S_NODE_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.nodeNameVolume Settings
spec:
containers:
- name: <container-name>
image: image: <your-registry>/<your-docker-image>:latest
volumeMounts:
- name: apm-attributes-k8s
mountPath: /etc/apm-attributes-k8s
volumes:
- name: apm-attributes-k8s
downwardAPI:
items:
- path: "labels"
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.labels
- path: "annotations"
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.annotationsIf the Kubernetes deployment does not have labels, annotations, or both, the Downward API for the same will cause an error when the application is deployed. In this case, you must remove the Downward API entry corresponding to metadata.labels, metadata.annotations, or both.
Deploy APM Java Agent using OpenTelemetry Operator
Here's information on how to deploy an APM Java agent using the OpenTelemetry operator to automatically inject and configure the APM Java agent into your Java application pods running on Kubernetes (K8s) clusters.
Figure 3-2 Deploy APM Java Agent using OpenTelemetry Operator
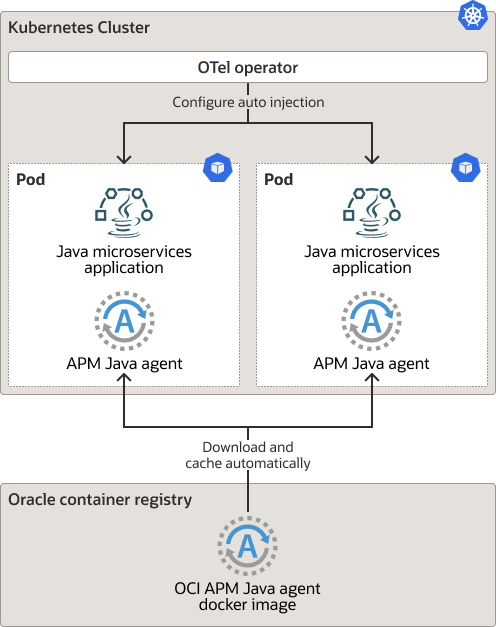
Recommendation:
Use this option if it's not possible to update the Docker container image and you prefer to make APM Java agent configuration changes using Kubernetes custom resource (CR) to automatically inject the APM agent into the JVMs at startup.
- For the Docker image versioning, avoid using the tag
:latestwhen deploying containers in production as it is harder to track which version of the image is running and more difficult to roll back properly. Instead, specify a meaningful tag such asv1.12.1.3. -
For Kubernetes, take backups of the Kubernetes custom resources (CRs) and configmaps.
Prerequisite: Install the OpenTelemetry Operator into the Kubernetes cluster.
There are three different options available: Operator release manifest, Operator helm chart, or Operator Hub.
In most cases, a cert-manager should be installed. If the helm chart option is used, there is an option to generate a self-signed cert instead.
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/cert-manager/cert-manager/releases/download/v1.14.2/cert-manager.yamlTo install the OpenTelemetry operator, run the following:
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/open-telemetry/opentelemetry-operator/releases/latest/download/opentelemetry-operator.yamlDeploy the APM Java agent
To deploy the APM Java agent, follow these steps:
- Create a Kubernetes Custom Resource (CR).
To manage automatic instrumentation, the OpenTelemetry Operator needs to be provided with information about the APM Java agent and its configuration which it's done using the Custom Resource Definition (CRD).
This Custom Resource will be used by the operator to copy the agent into the pod and add to it the required configuration.
To create the CR, run the following:kubectl apply -f - <<EOF apiVersion: opentelemetry.io/v1alpha1 kind: Instrumentation metadata: name: inst-apm-java namespace: opentelemetry-operator-system spec: java: image: container-registry.oracle.com/oci_observability_management/oci-apm-java-agent:1.15.0.516 env: - name: OTEL_com_oracle_apm_agent_data_upload_endpoint value: <data-upload-endpoint> - name: OTEL_com_oracle_apm_agent_private_data_key value: <private-data-key> EOFWhere:- <data-upload-endpoint> is the data upload endpoint URL that is generated when the APM domain is created. For information, see Obtain Data Upload Endpoint and Data Keys.
- <private-data-key> is the APM Java agent installation private data key which is generated when the APM domain is created. For information, see Obtain Data Upload Endpoint and Data Keys.
The created CR can be queried by running the following command:
All endpoints and environment variables required to be correct for auto-instrumentation to work properly.kubectl get otelinst -n opentelemetry-operator-system - Add the Kubernetes annotation.
The OpenTelemetry operator uses Kubernetes annotation to decide which pods should be auto-injected with the APM Java agent.
The annotation can be added to a namespace. In that case, all the pods within that namespace will get injected. The annotation can also be added to individual PodSpec objects, available as part of Deployment, Statefulset, and other resources.
Annotation:instrumentation.opentelemetry.io/inject-java: "opentelemetry-operator-system/inst-apm-java"To start editing your namespace, do the following:- Run the command:
kubectl edit namespace <your-namespace-name> - Edit the namespace once the editor is opened. For example,
vieditor. - Add the annotation to the namespace. Keep in mind indentation is very important to make it as a valid YAML file.
Example:apiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: labels: kubernetes.io/metadata.name: mynamespace annotations: instrumentation.opentelemetry.io/inject-java: "opentelemetry-operator-system/inst-apm-java" name: mynamespace spec: - Run the command:
- Restart the Kubernetes pod.
To restart the pod where you want to auto-inject the APM Java agent, run the following:
kubectl delete pod <your-pod-name> -n <your-namespace-name> - Verify the Kubernetes pod.
To verify that your pod has been auto-injected with the APM Java agent after it was restarted, run the following:
kubectl get pod <your-pod-name> -n <your-namespace-name> -o yaml
You can now go to the next step: Verify APM Java Agent Deployment.
For more information about how to deploy an APM Java agent using OpenTelemetry Operator, check out the blog: Automatically deploy an APM Java agent in Kubernetes Environments using the OpenTelemetry Operator
Deploy APM Java Agent on a Mounted Volume
Here's information on how to deploy an APM Java agent in Oracle Container Engine for Kubernetes (OKE) using a mounted volume.
Figure 3-3 Deploy APM Java Agent on a Mounted Volume
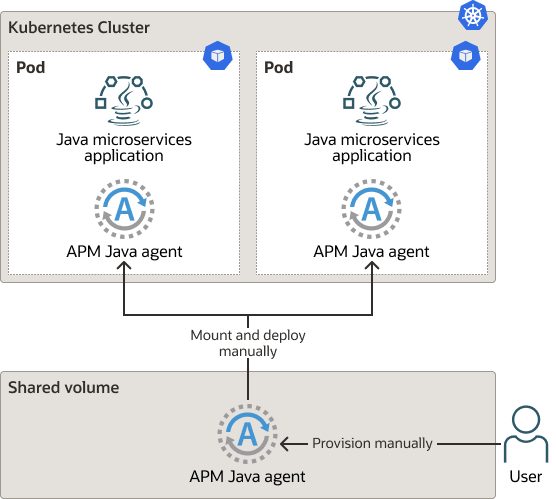
-
Use this option when it's not possible to make changes to the Docker container image and you prefer to use a shared mounted volume when changes to the APM Java agent are needed.
- Example 1: If you need to make frequent configuration changes to the APM agent then the container image requires to get updated, but it's not feasible to do it.
- Example 2: If the user who is deploying the APM agent does not have the required access or permissions to rebuild a container image.
-
For the docker image versioning, back up the binary and config files.
To deploy the APM Java agent on a mounted volume, follow these steps:
- Confirm you completed the APM Java agent prerequisite tasks.
Make a note of the data upload endpoint and data key when the APM Domain was created.
- Create a new file system that will mount the pods.
When creating the file system, it's important to ensure to select the same Virtual Cloud Network (VCN) Compartment that Kubernetes is using. Do the same for the Subnet Compartment.
- Mount the file system into the pods.
This step requires edits to the corresponding yaml files.
Create the
PersistentVolumeand related entities in Kubernetes, using the below yaml file. Note the following fields you need to edit for your environment:mntTargetId,serverandpath.kind: StorageClass apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: oci-fss provisioner: oracle.com/oci-fss parameters: mntTargetId: ocid1.mounttarget.oc1.iad.xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx --- apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolume metadata: name: oke-fsspv spec: storageClassName: oci-fss capacity: storage: 10Gi accessModes: - ReadWriteMany mountOptions: - nosuid nfs: # Replace this with the IP of your FSS file system in OCI server: 10.0.10.39 # Replace this with the Path of your FSS file system in OCI path: "/fss-for-kub" readOnly: false --- apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: oke-fsspvc spec: storageClassName: oci-fss accessModes: - ReadWriteMany resources: requests: # Although storage is provided here it is not used for FSS file systems storage: 10Gi volumeName: oke-fsspvTo apply the changes, run
kubectl apply -f <filename.yaml>Then, update the yaml file that manages the pods and add the volume and volume mount.
To take effect, recreate the pods.
- Download the APM Java agent file.
Download and copy the file to the mounted volume.
For download instructions, see Download the APM Java Agent Software.
After downloading, copy it to the mounted volume.
- Provision the APM Java Agent.
Log in to one of the containers to provision the APM Java Agent, locate the apm-java-agent-installer jar file and run the following:
java -jar ./apm-java-agent-installer-<version>.jar provision-agent -service-name=<Name of the Service> -destination=<Destination_Directory> -private-data-key=<Agent installation key generated during APM domain creation> -data-upload-endpoint=<dataUploadEndpoint URL generated during APM domain creation>For provisioning instructions, see Provision the APM Java Agent.
- Deploy the APM Java Agent.
Deploy the APM Java Agent by providing the oracle-apm-agent location to the microservice in the yaml file.
Add the
-javaagentargument and the APM agent jar file location to the java command of each microservice:java -javaagent:<Mounted Volume>/oracle-apm-agent/bootstrap/ApmAgent.jar - Restart Kubernetes.
Recreate the pods by running:
kubectl apply -f <filename.yaml>.You can now go to the next step: Verify APM Java Agent Deployment.
For more information about how to deploy an APM Java agent on a mounted volume, watch the video: Kubernetes Spring Boot Instrumentation for Distributed Tracing or check out the blog: Application Performance Monitoring: Instrument Java on Kubernetes for Monitoring and Diagnostics.