Scenario: Receiving Commands and Sending Responses using MQTTs
Use this scenario to receive commands in the cloud and send responses to a device using the MQTTs protocol to interact with your Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
Tasks
To complete the steps below, you can use an existing IoT domain and IoT domain group or create an IoT domain group and an IoT domain and then complete the following steps.
Step 1: Create a Digital Twin Instance
Using the CLI
- When you create a digital twin instance use a secret or a certificate so the digital twin instance can securely authenticate. You must create a secret or create a certificate to complete this scenario. Oracle recommends using one secret for each digital twin instance.
Use the
oci iot digital-twin-instance createcommand and required parameters to create a digital twin. The following example shows the command with the display name and authentication ID parameters:oci iot digital-twin-instance create --auth-id <vault-secret-or-client-certificate-id> --iot-domain-id <iot-domain-OCID>In this example response, notice the external key value. Use this external key value in Step 3: Use MQTTX to Connect Using an External ID:
"external-key": "<unique-id>"{ "data": { "auth-id": "<vault-secret-or-certificate-OCID>", "defined-tags": { "Oracle-Tags": { "CreatedBy": "default/user@oracle.com", "CreatedOn": "2025-08-05T18:03:15.264Z" } }, "description": null, "digital-twin-adapter-id": null, "digital-twin-model-id": null, "digital-twin-model-spec-uri": null, "display-name": "HVAC-instance", "external-key": "<unique-id>", "freeform-tags": {}, "id": "<iot-digital-twin-instance-OCID>", "iot-domain-id": "<iot-domain-OCID>", "lifecycle-state": "ACTIVE", "system-tags": {}, "time-created": "2025-08-05T18:03:15.870000+00:00", "time-updated": "2025-08-05T18:03:15.870000+00:00" }, "etag": "<unique-id>" }
Step 2: Define the Command in a JSON file
You can define the command in a JSON file and use this file in the next step.
The command.json file in this example contains the following commands to invoke the command and process the response according to instructions in the file.
{
"requestEndpoint": "/endpoints/1234",
"requestDuration": "PT3M",
"requestDataFormat": "JSON",
"requestData": {
"temp": 33
},
"requestDataContentType": "application/json",
"responseEndpoint": "/endpoints/4321",
"responseDuration": "PT3M"
}requestEndpoint: The URL path/endpoints/1234where the request will be sent. This is typically an API endpoint or an address where the IoT Platform listens for commands.requestDuration: The allowed or requested duration for the request to complete, in ISO 8601 duration format.PT3Mwhich equals 3 minutes.requestDataFormat: Specifies the date format for the data sent in the JSON request.requestData: The JSON payload that's sent with a key value pair to set a temperature value on the device:"temp": 33
Step 3: Invoke a Raw JSON Command on a Device
You can use the CLI or the API to invoke a command on a device, the following example uses the CLI.
Using the CLI
Use the oci iot digital-twin-instance invoke-raw-json-command command and parameters to invoke a raw JSON command on a device.
Replace the <digital-twin-instance-OCID> with the digital twin instance OCID from Step 1: Create a Digital Twin Instance. This example shows a request for a temperature value from the device using raw JSON command defined in the command.json file defined in Step 2: Define the Command in a JSON file.
oci iot digital-twin-instance invoke-raw-json-command --digital-twin-instance-id <digital-twin-instance-OCID> --request-endpoint "/endpoints/1234" --from-json --file://command.jsonStep 4: Use MQTTX to Connect to the Device Using an External ID
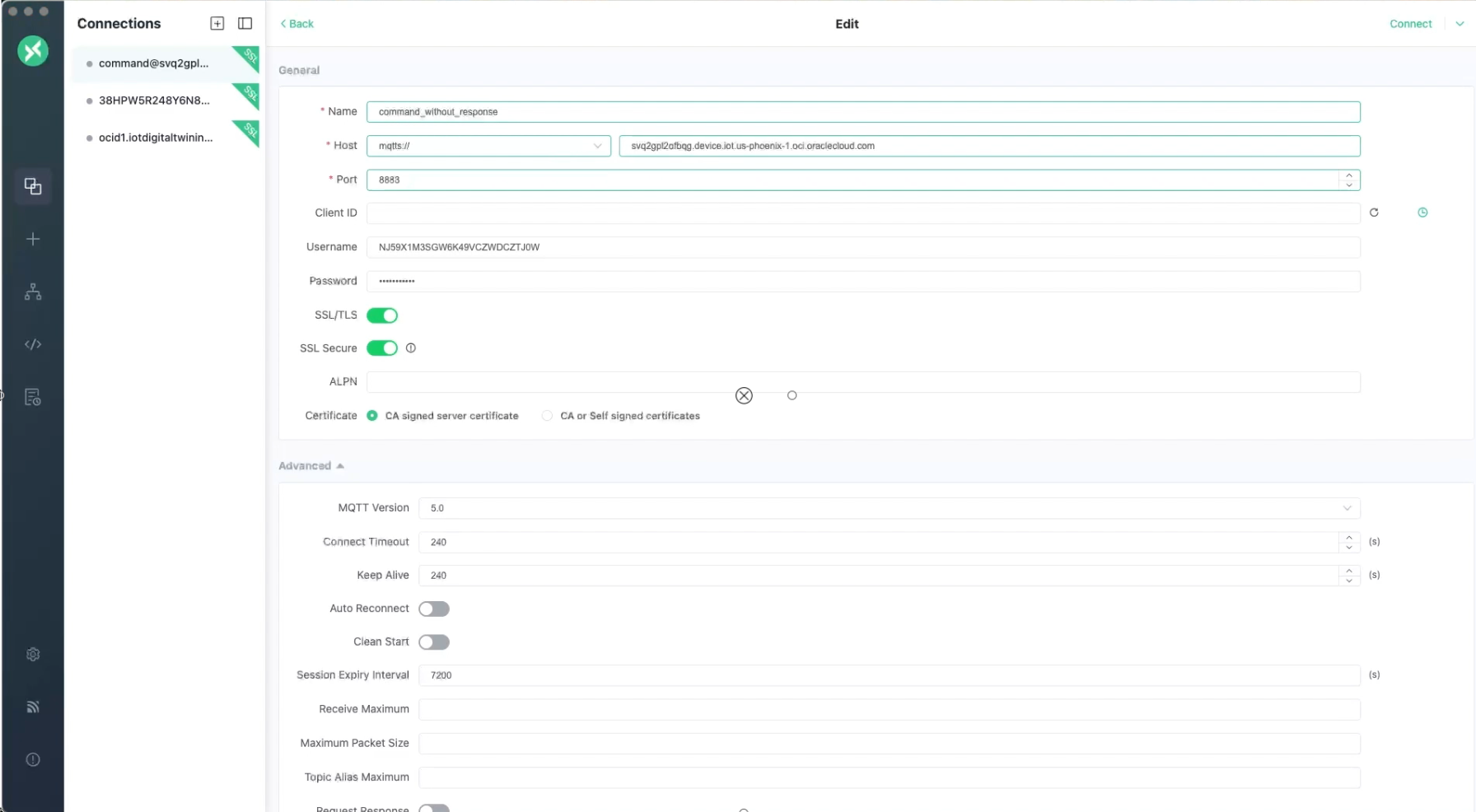
- Download and set up MQTTX follow these instructions, see Getting Started with MQTTX. Open MQTTX.
- Select + New Connection, to create a new connection.
- Enter the external key
<unique-id>value as the Username. You can find the external key in theoci iot digital-twin-instance createresponse, from the previous Step 1: Create a Digital Twin Instance:"external-key": "<unique-id>" - Enter the device password.
- Enter the Host. Select the
mqtts://protocol from the host drop-down list and enter the device host:<domain-short-id>.device.iot.<region>.oci.oraclecloud.comfrom the IoT domain. - Enter the port, for example:
8883 - Turn on the toggle SSL/TLS.
- Turn on the toggle SSL Secure.
- For the Certificate, select the CA signed server certificate option.
- When you configure the MQTTX connection make sure to connect using a
clean sessionand set theLast-Will-Retainoption tofalseto allow client subscriptions to be retained if the device briefly disconnects. - Set the Last Will QoS to 1.
- Select Connect.
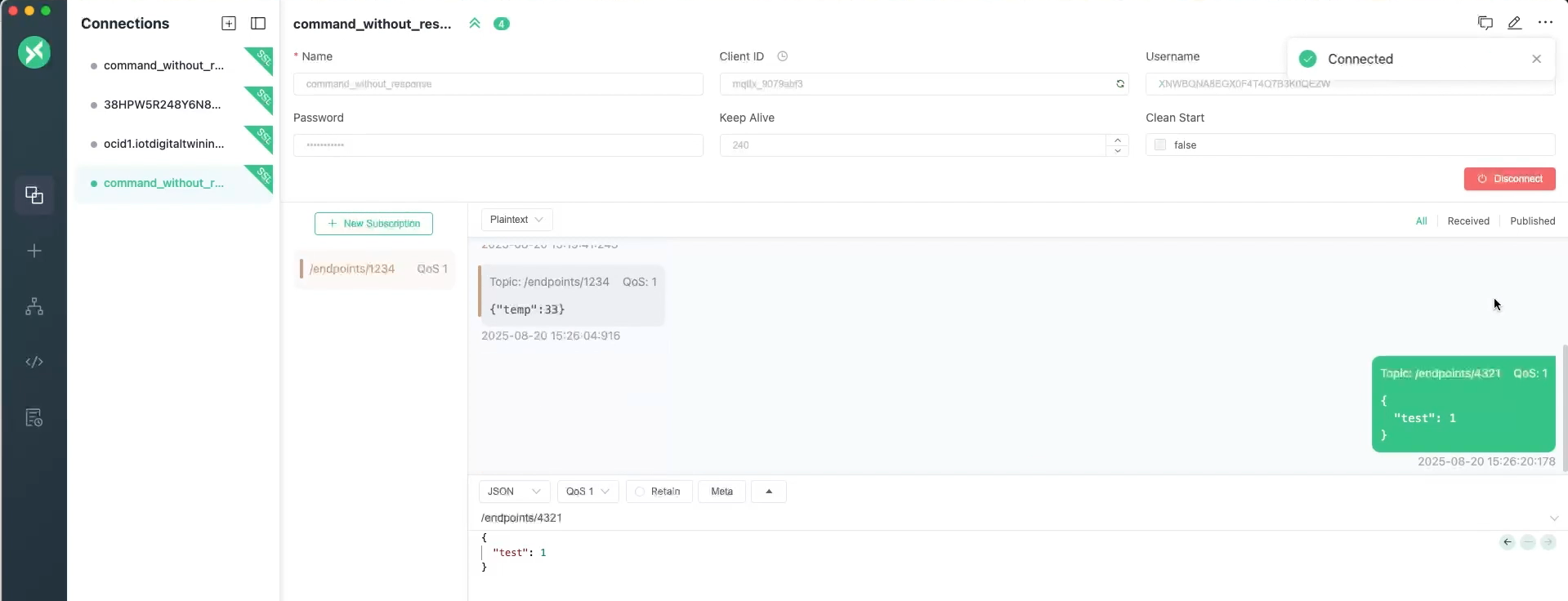
This image shows the settings in MQTTX, right click and open in a new tab to view a larger screenshot.
To view a larger screenshot, right click and open in a new tab.
Step 5: Subscribe to a Topic to Receive Responses in MQTTX
When the external system or IoT device publishes a message to the subscribed topic, you view the incoming messages in MQTTX under that topic. If you are awaiting a response from a prior command, ensure you are subscribed to the correct response topic that's dynamically set in digital twin instance response as the <external-id> value.
- In MQTTX, select + New Subscription.
- Enter the endpoint as the Topic.
- From QoS drop-down menu, select 1 At least once.
- Select Confirm.
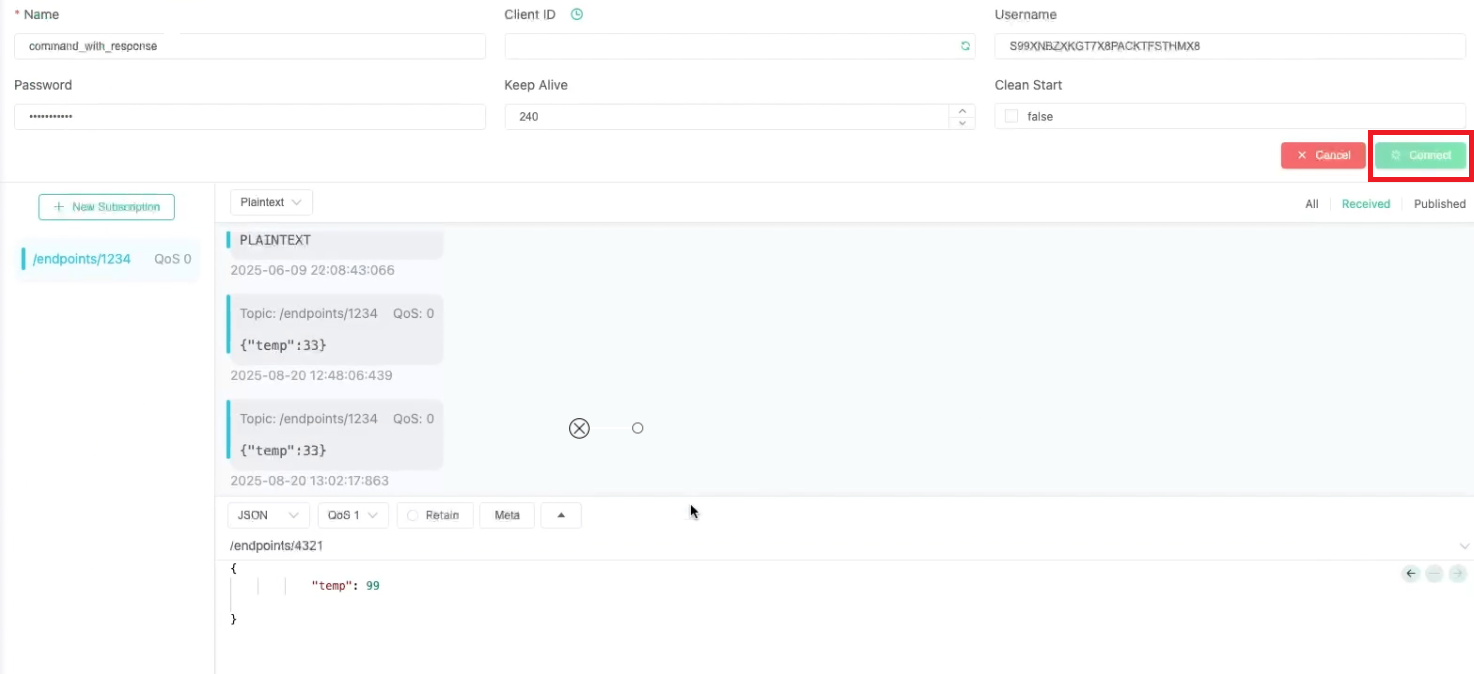
- Client ID: your-client-id
- Username: External ID.
- Password: Enter the device password.
- Enter
mqtts://with the device host and port number:mqtts://<iot-domain-short-id>.device.iot.<region>.oci.oraclecloud.com:8883
To view a larger screenshot, right click and open in a new tab.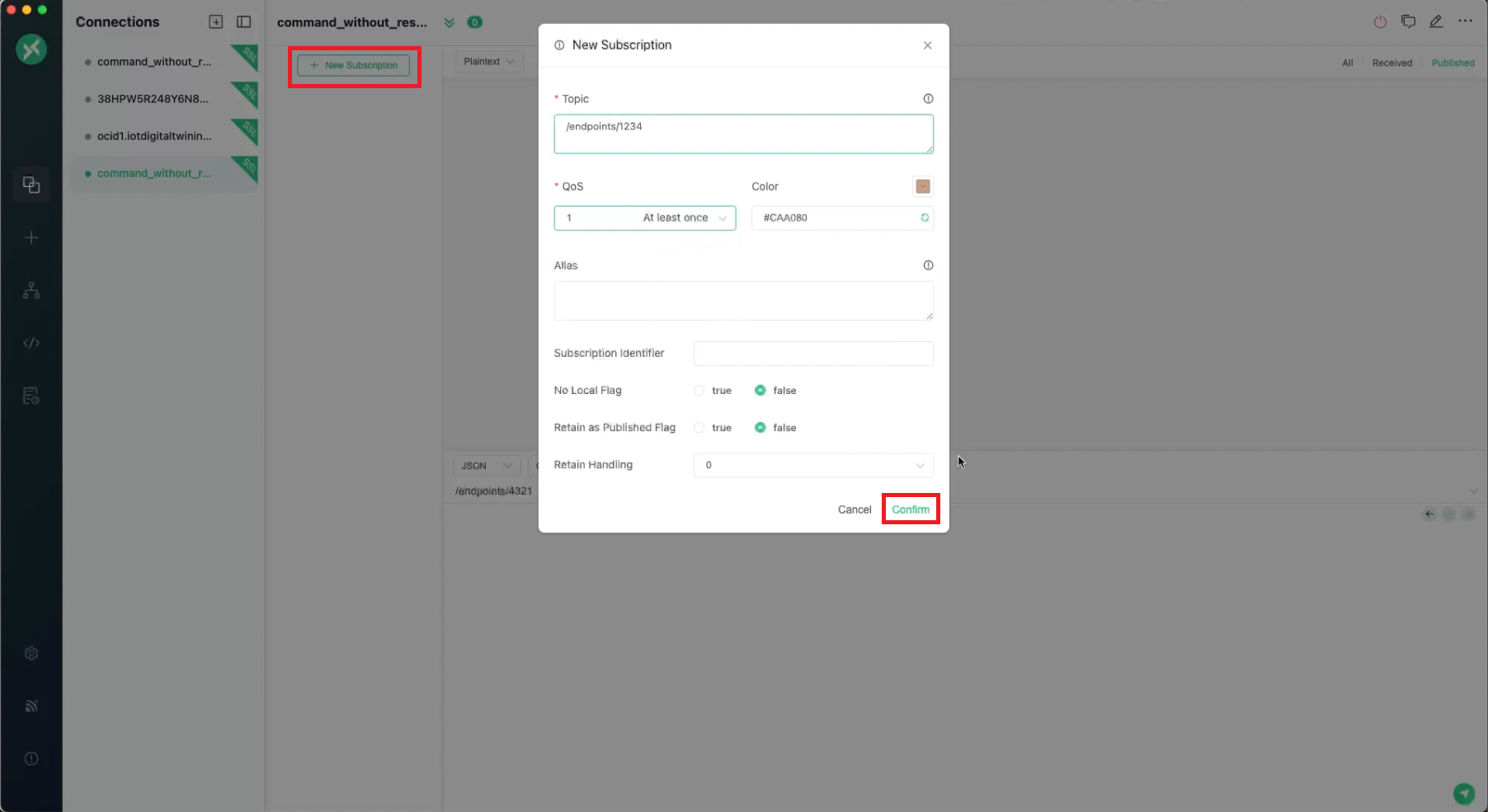
Step 6: Monitor the Command's Delivery Status in APEX
To view your IoT data in APEX requires configuring access to your data. After that configuration is complete, you can use APEX to work with your IoT data.
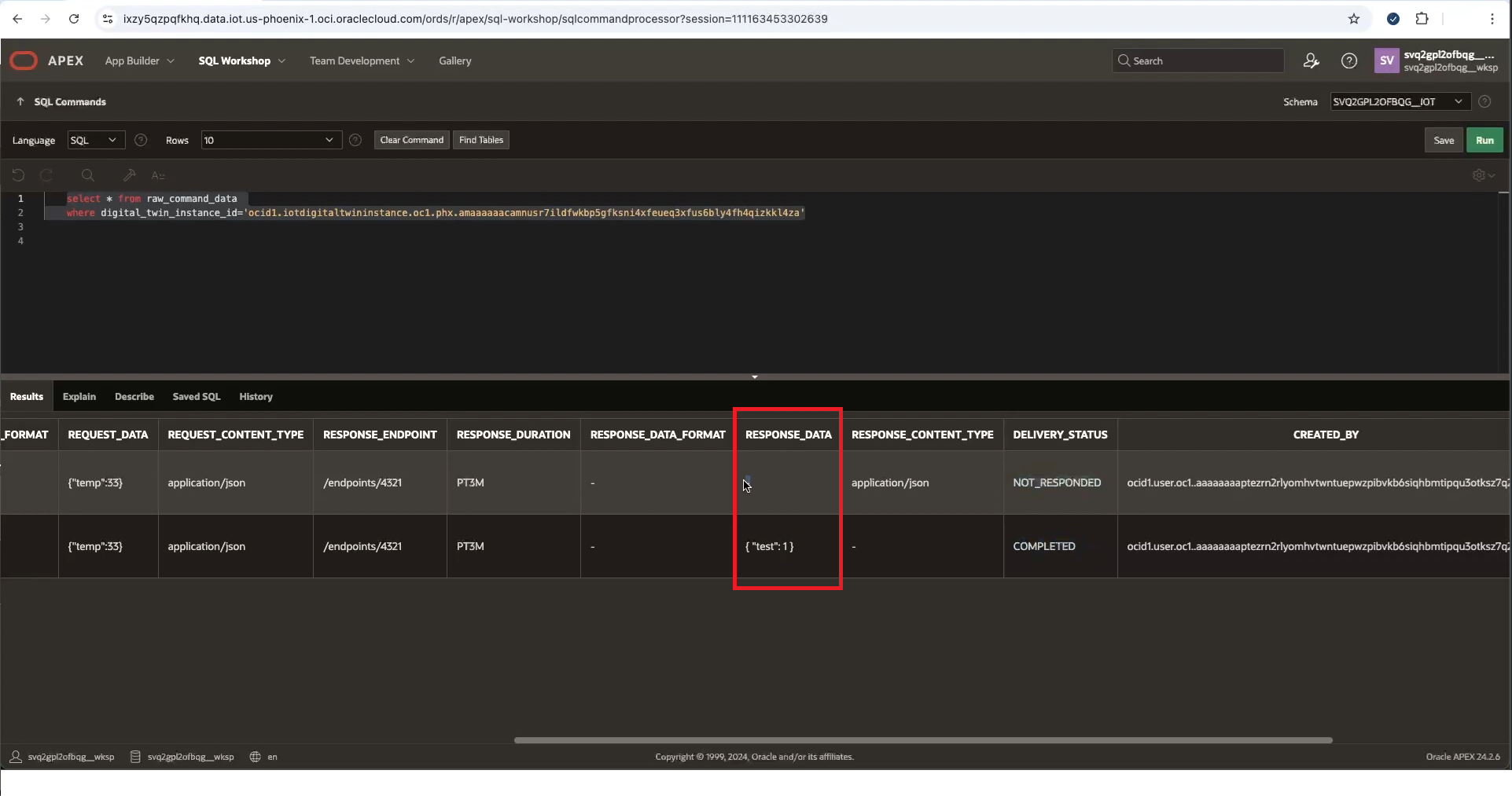
- In APEX, log in to the specific IoT domain's Workspace using the following as the workspace name and database user name. Notice the two underscores in the database schema name:Go to SQL Workshop and select SQL Commands to query the IoT data.
<domain-short-id-from-device-host>__IOT - Enter the following command, replace
<digital-twin-instance-OCID>with the digital twin OCID and select Run to query the raw command data:select * from raw_command_data where digital_twin_instance_id='<digital-twin-instance-OCID>' - In the Results, view the RESPONSE_DATA:
{"test":1}
Step 7: View the Command's Response in MQTTX
{
"test": 1
}To view a larger screenshot, right click and open in a new tab.