Metrics and Performance Testing
Observe performance for the Balanced elastic performance configuration option and learn about the host maximum.
For more information about FIO command samples you can use for performance testing see Sample FIO Commands for Block Volume Performance Tests on Linux-Based Instances.
Testing Methodology and Performance for Balanced Elastic Performance Option
- Before running any tests, protect your data by making a backup of your data and operating system environment to prevent any data loss.
- Don't run FIO tests directly against a device that's already in use, such as /dev/sdX. If it's in use as a formatted disk and data on it, running FIO with a write workload (readwrite, randrw, write, trimwrite) overwrites the data on the disk and causes data corruption. Run FIO only on unformatted raw devices that aren't in use.
This section describes the setup of the test environments, the methodology, and the observed performance for the Balanced elastic performance configuration option. Some of the sample volume sizes tested were:
-
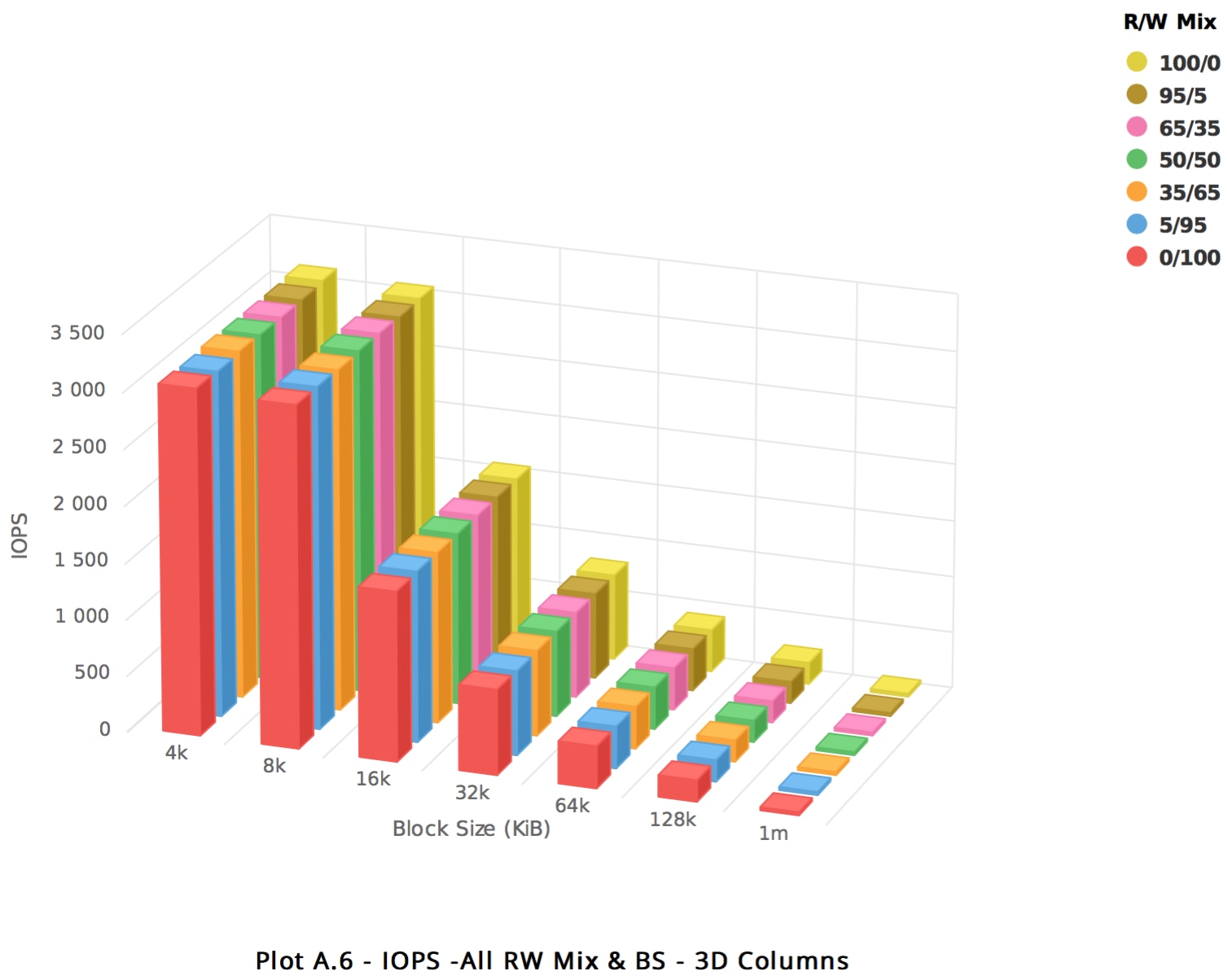
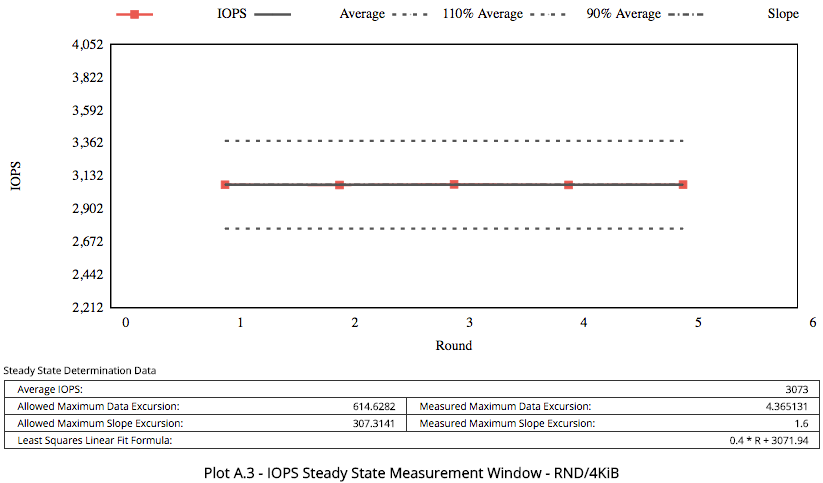
50 GB volume - 3,000 IOPS @ 4K
-
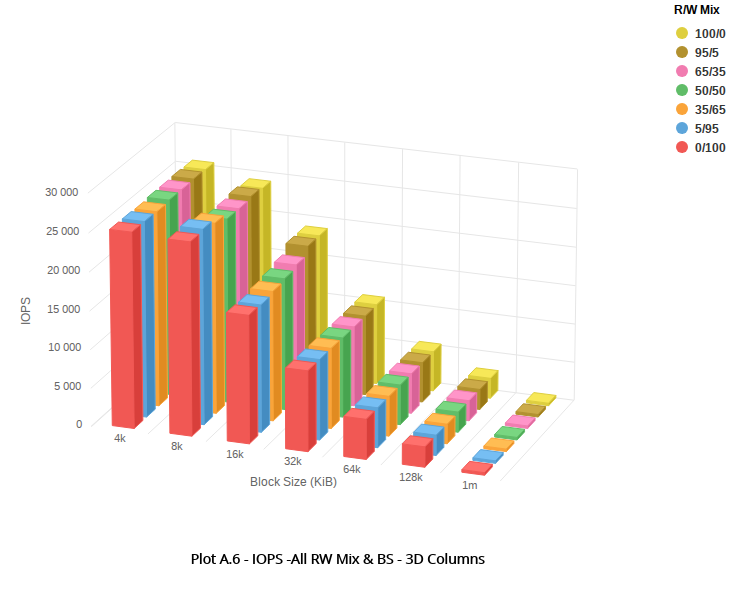
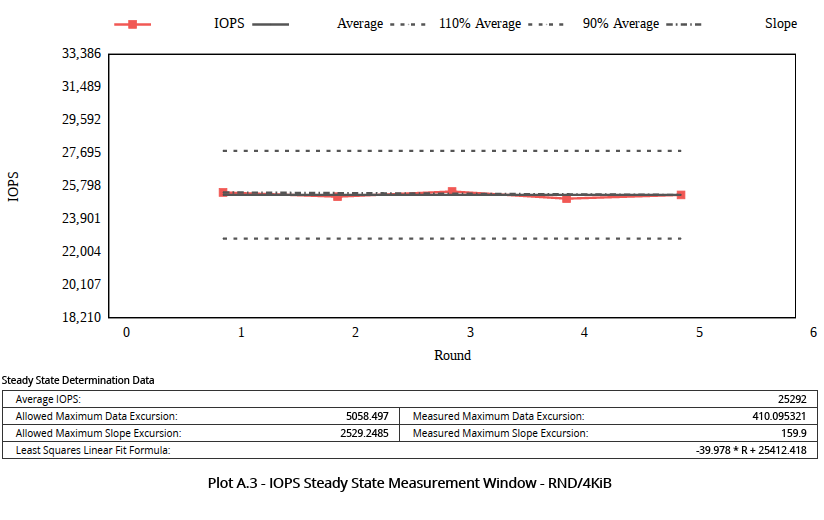
1 TB volume - 25,000 IOPS @ 4K
-
Host maximum, Ashburn (IAD) region, twenty 1 TB volumes - 400,000 IOPS @ 4K
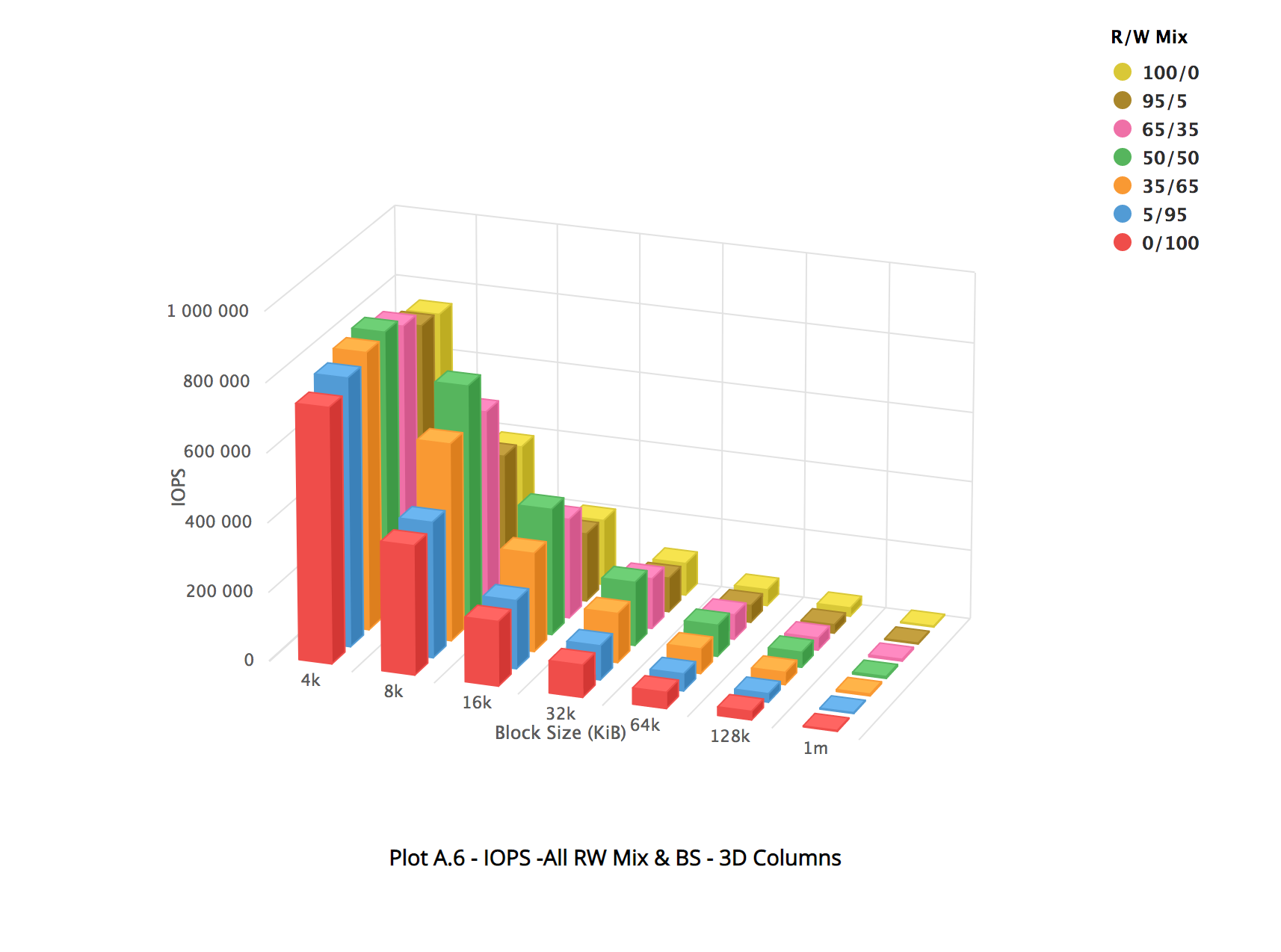
These tests used a wide range of volume sizes. To show the throughput performance limits, 256k or larger block sizes should be used. For most environments, 4K, 8K, or 16K blocks are common depending on the application workload, and these are used specifically for IOPS measurements.
In the observed performance images in this section, the X axis represents the volume size tested, ranging from 4KB to 1MB. The Y axis represents the IOPS delivered. The Z axis represents the read/write mix tested, ranging from 100% read to 100% write.
Performance Notes for Instance Types
-
The throughput performance results are for bare metal instances. Throughput performance on VM instances depends on the network bandwidth that's available to the instance, and further limited by that bandwidth for the volume. For details about the network bandwidth available for VM shapes, see the Network Bandwidth column in the VM Shapes table.
-
IOPS performance is independent of the instance type or shape, so is applicable to all bare metal and VM shapes, for iSCSI attached volumes.
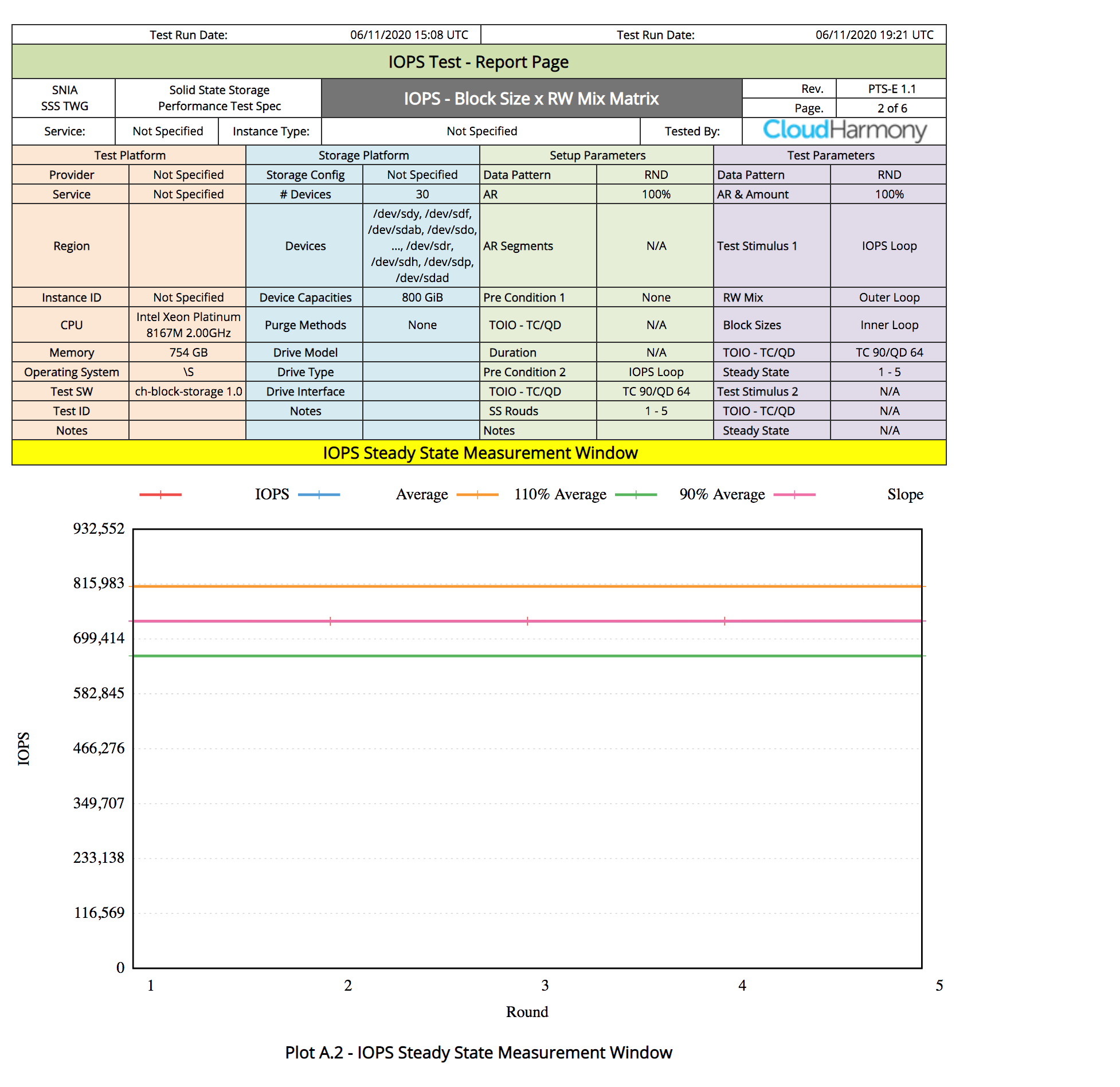
1 TB Block Volume
A 1 TB volume was mounted to a bare metal instance running in the Phoenix region. The instance shape was dense, workload was direct I/O with 10GB working set. See Sample FIO Commands for Block Volume Performance Tests on Linux-Based Instances for details on how to run performance benchmark tests.
The results showed that for 1 TB, the bandwidth limit for the larger block size test occurs at 320MBS.
The following images show the observed performance for 1 TB:
50 GB Block Volume
A 50 GB volume was mounted to a bare metal instance running in the Phoenix region. The instance shape was dense, workload was direct I/O with 10GB working set. See Sample FIO Commands for Block Volume Performance Tests on Linux-Based Instances for details on how to run performance benchmark tests.
The results showed that for the 50 GB volume, the bandwidth limit is confirmed as 24,000 KBPS for the larger block size tests (256 KB or larger block sizes), and the maximum of 3,000 IOPS at 4K block size is delivered. For small volumes, a 4K block size is common.
The following images show the observed performance for 50 GB:
Host Maximum
Depending on the instance shape, a single instance with multiple attached volumes can achieve performance of up to 800,000 IOPS when the elastic performance settings for the attached volumes are set to balanced or higher performance.
See Sample FIO Commands for Block Volume Performance Tests on Linux-Based Instances for details on how to run performance benchmark tests.
The following images show the observed performance: